Page 228 - Water and wastewater engineering
P. 228
COAGULATION AND FLOCCULATION 6-5
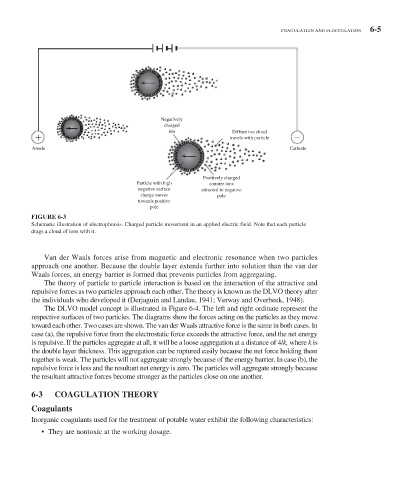
Negatively
charged
ion Diffuse ion cloud
travels with particle
Anode Cathode
Positively charged
Particle with high counter ions
negative surface attracted to negative
charge moves pole
towards positive
pole
FIGURE 6-3
Schematic illustration of electrophorsis. Charged particle movement in an applied electric field. Note that each particle
drags a cloud of ions with it.
Van der Waals forces arise from magnetic and electronic resonance when two particles
approach one another. Because the double layer extends further into solution than the van der
Waals forces, an energy barrier is formed that prevents particles from aggregating.
The theory of particle to particle interaction is based on the interaction of the attractive and
repulsive forces as two particles approach each other. The theory is known as the DLVO theory after
the individuals who developed it (Derjaguin and Landau, 1941; Verway and Overbeek, 1948).
The DLVO model concept is illustrated in Figure 6-4 . The left and right ordinate represent the
respective surfaces of two particles. The diagrams show the forces acting on the particles as they move
toward each other. Two cases are shown. The van der Waals attractive force is the same in both cases. In
case (a), the repulsive force from the electrostatic force exceeds the attractive force, and the net energy
is repulsive. If the particles aggregate at all, it will be a loose aggregation at a distance of 4/ k, where k is
the double layer thickness. This aggregation can be ruptured easily because the net force holding them
together is weak. The particles will not aggregate strongly because of the energy barrier. In case (b), the
repulsive force is less and the resultant net energy is zero. The particles will aggregate strongly because
the resultant attractive forces become stronger as the particles close on one another.
6-3 COAGULATION THEORY
Coagulants
Inorganic coagulants used for the treatment of potable water exhibit the following characteristics:
• They are nontoxic at the working dosage.