Page 231 - Water and wastewater engineering
P. 231
6-8 WATER AND WASTEWATER ENGINEERING
Compression of the Double Layer. If the electric double layer is compressed, the repulsive
force is reduced and particles will come together as a result of Brownian motion and remain
attached due to van der Waals forces of attraction. Both the ionic strength and the charge of coun-
terions are important in the compression of the double layer.
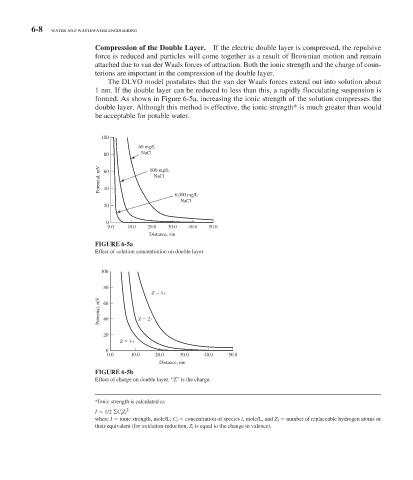
The DLVO model postulates that the van der Waals forces extend out into solution about
1 nm. If the double layer can be reduced to less than this, a rapidly flocculating suspension is
formed. As shown in Figure 6-5 a, increasing the ionic strength of the solution compresses the
double layer. Although this method is effective, the ionic strength * is much greater than would
be acceptable for potable water.
100
60 mg/L
80 NaCl
Potential, mV 60 600 mg/L
NaCl
40
6,000 mg/L
NaCl
20
0
0.0 10.0 20.0 30.0 40.0 50.0
Distance, nm
FIGURE 6-5a
Effect of solution concentration on double layer.
100
80
Z 1
Potential, mV 60 Z 2
40
20
Z 3
0
0.0 10.0 20.0 30.0 40.0 50.0
Distance, nm
FIGURE 6-5b
Effect of charge on double layer. “Z” is the charge.
*Ionic strength is calculated as
2
I 1/2 C i Z i
where I ionic strength, mole/L; C i concentration of species i, mole/L, and Z i number of replaceable hydrogen atoms or
their equivalent (for oxidation-reduction, Z i is equal to the change in valence).