Page 304 - Water and wastewater engineering
P. 304
LIME–SODA SOFTENING 7-21
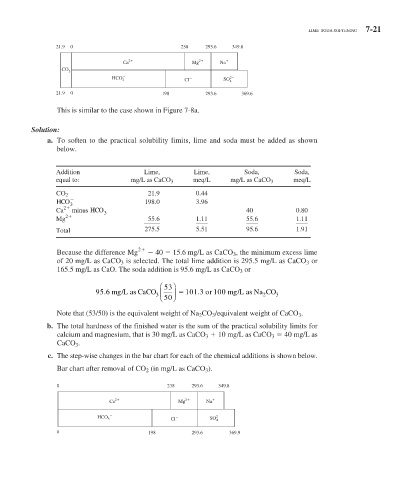
21.9 0 238 293.6 349.8
Ca 2 Mg 2 Na
CO 2
HCO SO 2
3 Cl 4
21.9 0 198 293.6 369.6
This is similar to the case shown in Figure 7-8a .
Solution:
a. To soften to the practical solubility limits, lime and soda must be added as shown
below.
Addition Lime, Lime, Soda, Soda,
equal to: mg/L as CaCO 3 meq/L mg/L as CaCO 3 meq/L
CO 2 21.9 0.44
HCO 198.0 3.96
3
2
Ca minus HCO 3 40 0.80
2
Mg 55.6 1.11 55.6 1.11
Total 275.5 5.51 95.6 1.91
2
Because the difference Mg 40 15.6 mg/L as CaCO 3 , the minimum excess lime
of 20 mg/L as CaCO 3 is selected. The total lime addition is 295.5 mg/L as CaCO 3 or
165.5 mg/L as CaO. The soda addition is 95.6 mg/L as CaCO 3 or
⎛ 53⎞
95 6 mg/L as CaCO 3 ⎜ ⎝ 50⎠ ⎟ 101 3 . or 100 mgg/L as Na CO 3
.
2
Note that (53/50) is the equivalent weight of Na 2 CO 3 /equivalent weight of CaCO 3 .
b. The total hardness of the finished water is the sum of the practical solubility limits for
calcium and magnesium, that is 30 mg/L as CaCO 3 10 mg/L as CaCO 3 40 mg/L as
CaCO 3 .
c. The step-wise changes in the bar chart for each of the chemical additions is shown below.
Bar chart after removal of CO 2 (in mg/L as CaCO 3 ).
0 238 293.6 349.8
2 2
Ca Mg Na
HCO 3 Cl SO 2
4
0 198 293.6 369.9