Page 301 - Water and wastewater engineering
P. 301
7-18 WATER AND WASTEWATER ENGINEERING
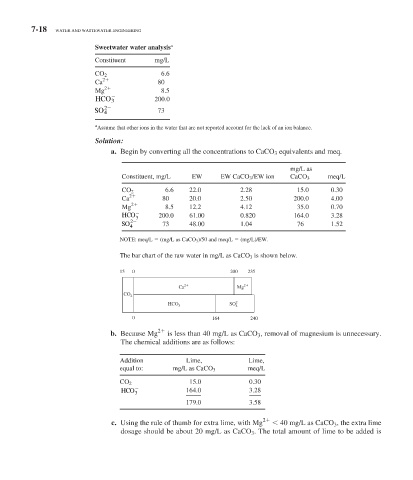
Sweetwater water analysis a
Constituent mg/L
6.6
CO 2
Ca 2 80
Mg 2 8.5
HCO 3 200.0
2
SO 4 73
a
Assume that other ions in the water that are not reported account for the lack of an ion balance.
Solution:
a. Begin by converting all the concentrations to CaCO 3 equivalents and meq.
mg/L as
Constituent, mg/L EW EW CaCO 3 /EW ion CaCO 3 meq/L
6.6 22.0 2.28 15.0 0.30
CO 2
Ca 2 80 20.0 2.50 200.0 4.00
Mg 2 8.5 12.2 4.12 35.0 0.70
HCO 200.0 61.00 0.820 164.0 3.28
3
2
SO 4 73 48.00 1.04 76 1.52
NOTE: meq/L (mg/L as CaCO 3 )/50 and meq/L (mg/L)/EW.
The bar chart of the raw water in mg/L as CaCO 3 is shown below.
15 0 200 235
Ca 2 Mg 2
CO 2
HCO SO 2
4
3
0 164 240
2
b. Because Mg is less than 40 mg/L as CaCO 3 , removal of magnesium is unnecessary.
The chemical additions are as follows:
Addition Lime, Lime,
equal to: mg/L as CaCO 3 meq/L
CO 2 15.0 0.30
HCO 164.0 3.28
3
179.0 3.58
2
c. Using the rule of thumb for extra lime, with Mg 40 mg/L as CaCO 3 , the extra lime
dosage should be about 20 mg/L as CaCO 3 . The total amount of lime to be added is