Page 325 - Water and wastewater engineering
P. 325
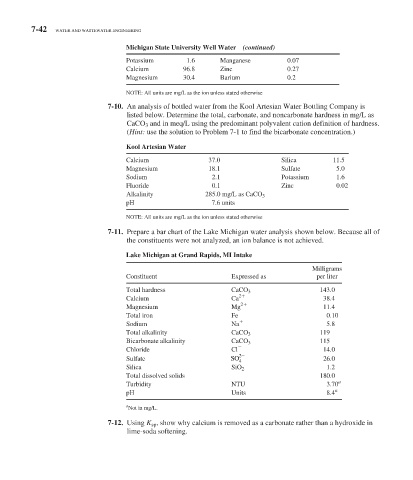
7-42 WATER AND WASTEWATER ENGINEERING
Michigan State University Well Water (continued)
Potassium 1.6 Manganese 0.07
Calcium 96.8 Zinc 0.27
Magnesium 30.4 Barium 0.2
NOTE: All units are mg/L as the ion unless stated otherwise
7-10. An analysis of bottled water from the Kool Artesian Water Bottling Company is
listed below. Determine the total, carbonate, and noncarbonate hardness in mg/L as
CaCO 3 and in meq/L using the predominant polyvalent cation definition of hardness.
( Hint: use the solution to Problem 7-1 to find the bicarbonate concentration.)
Kool Artesian Water
Calcium 37.0 Silica 11.5
Magnesium 18.1 Sulfate 5.0
Sodium 2.1 Potassium 1.6
Fluoride 0.1 Zinc 0.02
Alkalinity 285.0 mg/L as CaCO 3
pH 7.6 units
NOTE: All units are mg/L as the ion unless stated otherwise
7-11. Prepare a bar chart of the Lake Michigan water analysis shown below. Because all of
the constituents were not analyzed, an ion balance is not achieved.
Lake Michigan at Grand Rapids, MI Intake
Milligrams
Constituent Expressed as per liter
Total hardness CaCO 3 143.0
Calcium Ca 2 38.4
Magnesium Mg 2 11.4
Total iron Fe 0.10
Sodium Na 5.8
Total alkalinity CaCO 3 119
Bicarbonate alkalinity CaCO 3 115
Chloride Cl 14.0
2
Sulfate SO 4 26.0
Silica SiO 2 1.2
Total dissolved solids 180.0
Turbidity NTU 3.70 a
pH Units 8.4 a
a
Not in mg/L.
7-12. Using K sp , show why calcium is removed as a carbonate rather than a hydroxide in
lime-soda softening.