Page 449 - Water and wastewater engineering
P. 449
11-22 WATER AND WASTEWATER ENGINEERING
addition, and good settling, dual-media filters can readily achieve satisfactory results at filtra-
3
2
3
2
tion rates up to 25 m /h · m of surface area (25 m/h or 600 m /d · m ). However, filter effluent
2
3
quality tends to degrade at filtration rates above 12.5 m/h (300 m /d · m ) with weak alum floc
without polymer (MWH, 2005).
Generally, conservative design filtration rates are 7.5 m/h for rapid sand filters, 15 m/h for
dual-media filters, and 25 m/h for deep, coarse monomedium filters that have polymer added as a
filter aid. Approximate clean bed headlosses for common filter beds and filtration rates are given
in Table 11-3 .
Dimensions. The area of a filter bed may be estimated as
Q
A (11-18)
Nq
2
where A area of a bed, m
3
Q maximum day flow rate, m /d
N number of beds
3 2
q filtration rate, m /d · m
2
Although some extremely large plants may employ filter areas up to 200 m , a common upper
2 2
bound for large plants is 100 m . The general range in area is 25 to 100 m with an average of
2
about 50 m (Kawamura, 2000; MWH, 2005).
Filters are generally composed of two cells per filter box to form a bed. Generally, the gul-
let bisects the box to form the two cells. The width of a filter cell should be less than 6 m so that
“off-the-shelf” wash water troughs may be used. The suggested length-to-width ratio of a cell is
in the range of 2:1 to 4:1 (Kawamura, 2000).
The filter box depth is on the order of 4 to 8 m to provide space for the underdrain system,
media, and headloss. Due to construction costs, filter designs rarely provide more than 2 to 3 m of
available head through the filter bed. Experience indicates that effluent turbidity begins to increase
when the net headloss is over 1.8 m for well-conditioned floc and dual-media filters, and may
be less than 0.8 m for poorly conditioned floc (Cleasby and Logsdon, 1999; Kawamura, 2000;
MWH, 2005).
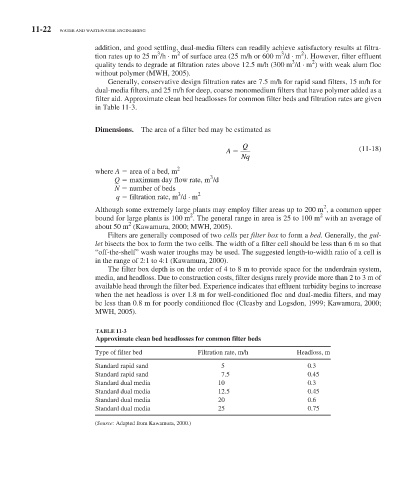
TABLE 11-3
Approximate clean bed headlosses for common filter beds
Type of filter bed Filtration rate, m/h Headloss, m
Standard rapid sand 5 0.3
Standard rapid sand 7.5 0.45
Standard dual media 10 0.3
Standard dual media 12.5 0.45
Standard dual media 20 0.6
Standard dual media 25 0.75
(Source: Adapted from Kawamura, 2000.)