Page 456 - Water and wastewater engineering
P. 456
GRANULAR FILTRATION 11-29
2
Sand
1.8
Garnet S.G. ~ 2.60 Anthracite coal
1.6 S.G. ~ 4.0 S.G. ~ 1.65 S.G. ~ 1.70
1.4
Backwash rate, m/min 1.2 1 S.G. ~ 1.55 S.G. ~ 1.60
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0
60% Weight grain size, mm
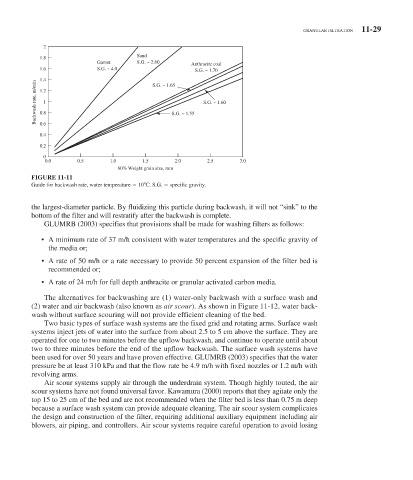
FIGURE 11-11
Guide for backwash rate, water temperature 10 C. S.G. specific gravity.
the largest-diameter particle. By fluidizing this particle during backwash, it will not “sink” to the
bottom of the filter and will restratify after the backwash is complete.
GLUMRB (2003) specifies that provisions shall be made for washing filters as follows:
• A minimum rate of 37 m/h consistent with water temperatures and the specific gravity of
the media or;
• A rate of 50 m/h or a rate necessary to provide 50 percent expansion of the filter bed is
recommended or;
• A rate of 24 m/h for full depth anthracite or granular activated carbon media.
The alternatives for backwashing are (1) water-only backwash with a surface wash and
(2) water and air backwash (also known as air scour ). As shown in Figure 11-12 , water back-
wash without surface scouring will not provide efficient cleaning of the bed.
Two basic types of surface wash systems are the fixed grid and rotating arms. Surface wash
systems inject jets of water into the surface from about 2.5 to 5 cm above the surface. They are
operated for one to two minutes before the upflow backwash, and continue to operate until about
two to three minutes before the end of the upflow backwash. The surface wash systems have
been used for over 50 years and have proven effective. GLUMRB (2003) specifies that the water
pressure be at least 310 kPa and that the flow rate be 4.9 m/h with fixed nozzles or 1.2 m/h with
revolving arms.
Air scour systems supply air through the underdrain system. Though highly touted, the air
scour systems have not found universal favor. Kawamura (2000) reports that they agitate only the
top 15 to 25 cm of the bed and are not recommended when the filter bed is less than 0.75 m deep
because a surface wash system can provide adequate cleaning. The air scour system complicates
the design and construction of the filter, requiring additional auxiliary equipment including air
blowers, air piping, and controllers. Air scour systems require careful operation to avoid losing