Page 102 - Welding Robots Technology, System Issues, and Applications
P. 102
Welding Robots
88
Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) is widely used in welding applications because
of the specific advantages it offers such as reduced spatter and smoother bead
appearance as compared with submerged arc welding. There are two stable metal
transfer modes in GMAW: short-circuit metal transfer at low arc voltage; and spray
metal transfer at high voltage and high current.
In the field of GMAW of steel, both physical analysis of the welding process [7]-
[11] and statistical analysis of real welding signals have been performed [12]-[21].
However, the problem of classifying the weld with respect to quality is still in
focus for research and is an important area to produce efficient control systems
which include, if not all, the most important parameters and how these affect the
quality and productivity, and the proper definition of the corresponding WPS for
control purposes.
Short-circuiting transfer Globular transfer Spray transfer
50 40 50 50
Voltage (V) 30 20 40 30 20 40 30 20
0 10 10 10
0
10.45 10.46 10.47 10.48 10.49 10.5 10.51 10.52 10.53 10.54 10.55 10.45 10.46 10.47 10.48 10.49 10.5 10.51 10.52 10.53 10.54 10.55 10.45 10.46 10.47 10.48 10.49 10.5 10.51 10.52 10.53 10.54 10.55
0
400 400 400
Current (A) 300 300 300
200
200
200
100
100
0
10.45 10.46 10.47 10.48 10.49 10.5 10.51 10.52 10.53 10.54 10.55 0 100 0
10.45 10.46 10.47 10.48 10.49 10.5 10.51 10.52 10.53 10.54 10.55
10.45 10.46 10.47 10.48 10.49 10.5 10.51 10.52 10.53 10.54 10.55
Time (s)
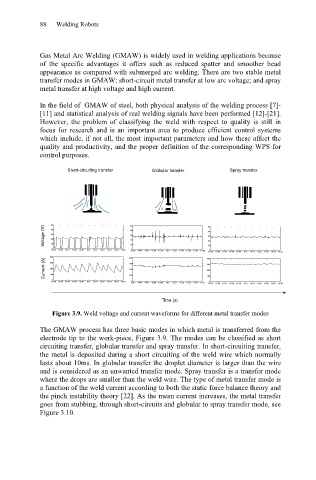
Figure 3.9. Weld voltage and current waveforms for different metal transfer modes
The GMAW process has three basic modes in which metal is transferred from the
electrode tip to the work-piece, Figure 3.9. The modes can be classified as short
circuiting transfer, globular transfer and spray transfer. In short-circuiting transfer,
the metal is deposited during a short circuiting of the weld wire which normally
lasts about 10ms. In globular transfer the droplet diameter is larger than the wire
and is considered as an unwanted transfer mode. Spray transfer is a transfer mode
where the drops are smaller than the weld wire. The type of metal transfer mode is
a function of the weld current according to both the static force balance theory and
the pinch instability theory [22]. As the mean current increases, the metal transfer
goes from stubbing, through short-circuits and globular to spray transfer mode, see
Figure 3.10.