Page 103 - Welding Robots Technology, System Issues, and Applications
P. 103
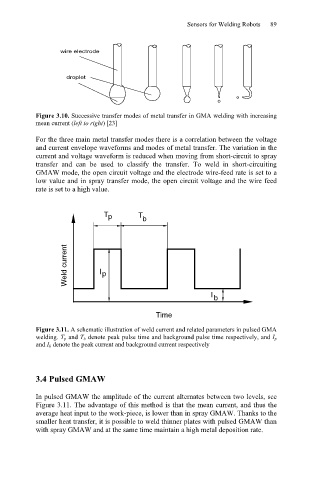
wire electrode
droplet Sensors for Welding Robots 89
Figure 3.10. Successive transfer modes of metal transfer in GMA welding with increasing
mean current (left to right) [23]
For the three main metal transfer modes there is a correlation between the voltage
and current envelope waveforms and modes of metal transfer. The variation in the
current and voltage waveform is reduced when moving from short-circuit to spray
transfer and can be used to classify the transfer. To weld in short-circuiting
GMAW mode, the open circuit voltage and the electrode wire-feed rate is set to a
low value and in spray transfer mode, the open circuit voltage and the wire feed
rate is set to a high value.
T p T b
Weld current I p
I
b
Time
Figure 3.11. A schematic illustration of weld current and related parameters in pulsed GMA
welding. T p and T b denote peak pulse time and background pulse time respectively, and I p
and I b denote the peak current and background current respectively
3.4 Pulsed GMAW
In pulsed GMAW the amplitude of the current alternates between two levels, see
Figure 3.11. The advantage of this method is that the mean current, and thus the
average heat input to the work-piece, is lower than in spray GMAW. Thanks to the
smaller heat transfer, it is possible to weld thinner plates with pulsed GMAW than
with spray GMAW and at the same time maintain a high metal deposition rate.