Page 99 - Welding Robots Technology, System Issues, and Applications
P. 99
straight motion. However, in medium to thick plates this is usually not a problem
(thicknesses above about 3 mm). Sensors for Welding Robots 85
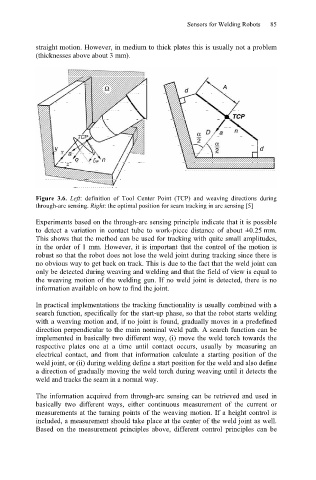
Figure 3.6. Left: definition of Tool Center Point (TCP) and weaving directions during
through-arc sensing. Right: the optimal position for seam tracking in arc sensing [5]
Experiments based on the through-arc sensing principle indicate that it is possible
to detect a variation in contact tube to work-piece distance of about ±0.25 mm.
This shows that the method can be used for tracking with quite small amplitudes,
in the order of 1 mm. However, it is important that the control of the motion is
robust so that the robot does not lose the weld joint during tracking since there is
no obvious way to get back on track. This is due to the fact that the weld joint can
only be detected during weaving and welding and that the field of view is equal to
the weaving motion of the welding gun. If no weld joint is detected, there is no
information available on how to find the joint.
In practical implementations the tracking functionality is usually combined with a
search function, specifically for the start-up phase, so that the robot starts welding
with a weaving motion and, if no joint is found, gradually moves in a predefined
direction perpendicular to the main nominal weld path. A search function can be
implemented in basically two different way, (i) move the weld torch towards the
respective plates one at a time until contact occurs, usually by measuring an
electrical contact, and from that information calculate a starting position of the
weld joint, or (ii) during welding define a start position for the weld and also define
a direction of gradually moving the weld torch during weaving until it detects the
weld and tracks the seam in a normal way.
The information acquired from through-arc sensing can be retrieved and used in
basically two different ways, either continuous measurement of the current or
measurements at the turning points of the weaving motion. If a height control is
included, a measurement should take place at the center of the weld joint as well.
Based on the measurement principles above, different control principles can be