Page 45 - Welding Robots Technology, System Issues, and Applications
P. 45
Welding Robots
30
of several elements [4],[5]. These electrodes have better operational characteristics
than thoriated electrodes and can be used in welding carbon and stainless steels,
nickel and titanium alloys. Zirconiated tungsten electrodes are excellent for AC
due to its good arc starting, high resistance to contamination and small tip shape
deterioration.
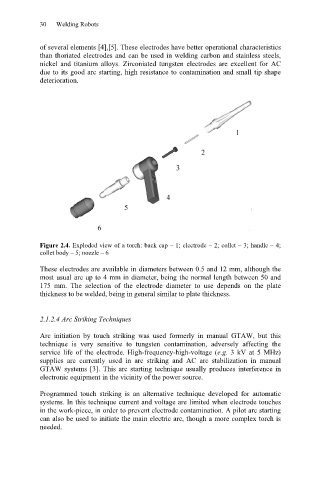
Figure 2.4. Exploded view of a torch: back cap – 1; electrode – 2; collet – 3; handle – 4;
collet body – 5; nozzle – 6
These electrodes are available in diameters between 0.5 and 12 mm, although the
most usual are up to 4 mm in diameter, being the normal length between 50 and
175 mm. The selection of the electrode diameter to use depends on the plate
thickness to be welded, being in general similar to plate thickness.
2.1.2.4 Arc Striking Techniques
Arc initiation by touch striking was used formerly in manual GTAW, but this
technique is very sensitive to tungsten contamination, adversely affecting the
service life of the electrode. High-frequency-high-voltage (e.g. 3 kV at 5 MHz)
supplies are currently used in arc striking and AC arc stabilization in manual
GTAW systems [3]. This arc starting technique usually produces interference in
electronic equipment in the vicinity of the power source.
Programmed touch striking is an alternative technique developed for automatic
systems. In this technique current and voltage are limited when electrode touches
in the work-piece, in order to prevent electrode contamination. A pilot arc starting
can also be used to initiate the main electric arc, though a more complex torch is
needed.