Page 44 - Welding Robots Technology, System Issues, and Applications
P. 44
Welding Technology
29
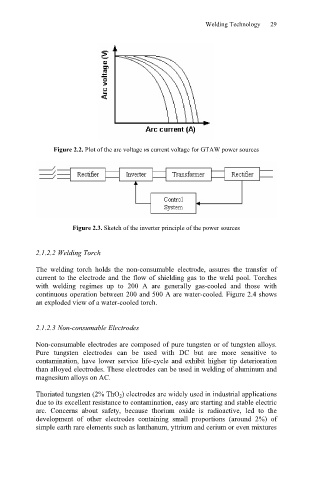
Figure 2.2. Plot of the arc voltage vs current voltage for GTAW power sources
Figure 2.3. Sketch of the inverter principle of the power sources
2.1.2.2 Welding Torch
The welding torch holds the non-consumable electrode, assures the transfer of
current to the electrode and the flow of shielding gas to the weld pool. Torches
with welding regimes up to 200 A are generally gas-cooled and those with
continuous operation between 200 and 500 A are water-cooled. Figure 2.4 shows
an exploded view of a water-cooled torch.
2.1.2.3 Non-consumable Electrodes
Non-consumable electrodes are composed of pure tungsten or of tungsten alloys.
Pure tungsten electrodes can be used with DC but are more sensitive to
contamination, have lower service life-cycle and exhibit higher tip deterioration
than alloyed electrodes. These electrodes can be used in welding of aluminum and
magnesium alloys on AC.
Thoriated tungsten (2% ThO 2) electrodes are widely used in industrial applications
due to its excellent resistance to contamination, easy arc starting and stable electric
arc. Concerns about safety, because thorium oxide is radioactive, led to the
development of other electrodes containing small proportions (around 2%) of
simple earth rare elements such as lanthanum, yttrium and cerium or even mixtures