Page 63 - Welding Robots Technology, System Issues, and Applications
P. 63
Welding Robots
48
The Laser beam can also be transmitted through fiber optics which leads to several
advantages, such as improved flexibility of laser systems and reduced need for
accurate mirror alignment.
cooling
system
excitation
pump light
Nd:YAG crystal
beam delivery
system
rear mirror output mirror
power supply
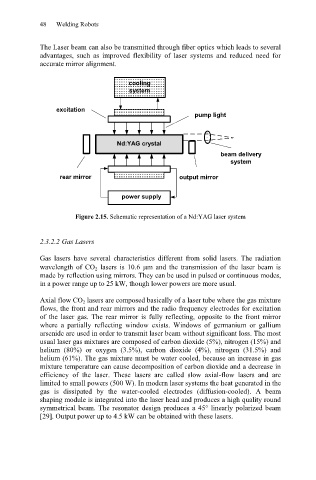
Figure 2.15. Schematic representation of a Nd:YAG laser system
2.3.2.2 Gas Lasers
Gas lasers have several characteristics different from solid lasers. The radiation
wavelength of CO 2 lasers is 10.6 Pm and the transmission of the laser beam is
made by reflection using mirrors. They can be used in pulsed or continuous modes,
in a power range up to 25 kW, though lower powers are more usual.
Axial flow CO 2 lasers are composed basically of a laser tube where the gas mixture
flows, the front and rear mirrors and the radio frequency electrodes for excitation
of the laser gas. The rear mirror is fully reflecting, opposite to the front mirror
where a partially reflecting window exists. Windows of germanium or gallium
arsenide are used in order to transmit laser beam without significant loss. The most
usual laser gas mixtures are composed of carbon dioxide (5%), nitrogen (15%) and
helium (80%) or oxygen (3.5%), carbon dioxide (4%), nitrogen (31.5%) and
helium (61%). The gas mixture must be water cooled, because an increase in gas
mixture temperature can cause decomposition of carbon dioxide and a decrease in
efficiency of the laser. These lasers are called slow axial-flow lasers and are
limited to small powers (500 W). In modern laser systems the heat generated in the
gas is dissipated by the water-cooled electrodes (diffusion-cooled). A beam
shaping module is integrated into the laser head and produces a high quality round
symmetrical beam. The resonator design produces a 45° linearly polarized beam
[29]. Output power up to 4.5 kW can be obtained with these lasers.