Page 64 - Welding Robots Technology, System Issues, and Applications
P. 64
Welding Technology
heat
system
exchanger cooling tangential blower 49
laser beam
output window
rear mirror
HF electrodes power supply output mirror
gas flow direction
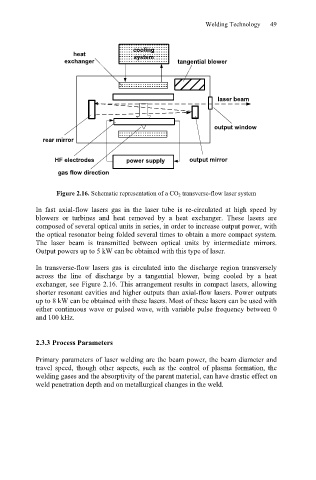
Figure 2.16. Schematic representation of a CO 2 transverse-flow laser system
In fast axial-flow lasers gas in the laser tube is re-circulated at high speed by
blowers or turbines and heat removed by a heat exchanger. These lasers are
composed of several optical units in series, in order to increase output power, with
the optical resonator being folded several times to obtain a more compact system.
The laser beam is transmitted between optical units by intermediate mirrors.
Output powers up to 5 kW can be obtained with this type of laser.
In transverse-flow lasers gas is circulated into the discharge region transversely
across the line of discharge by a tangential blower, being cooled by a heat
exchanger, see Figure 2.16. This arrangement results in compact lasers, allowing
shorter resonant cavities and higher outputs than axial-flow lasers. Power outputs
up to 8 kW can be obtained with these lasers. Most of these lasers can be used with
either continuous wave or pulsed wave, with variable pulse frequency between 0
and 100 kHz.
2.3.3 Process Parameters
Primary parameters of laser welding are the beam power, the beam diameter and
travel speed, though other aspects, such as the control of plasma formation, the
welding gases and the absorptivity of the parent material, can have drastic effect on
weld penetration depth and on metallurgical changes in the weld.