Page 69 - Welding Robots Technology, System Issues, and Applications
P. 69
Welding Robots
54
laser bar optical system
diode stack
focus
cooling sistem
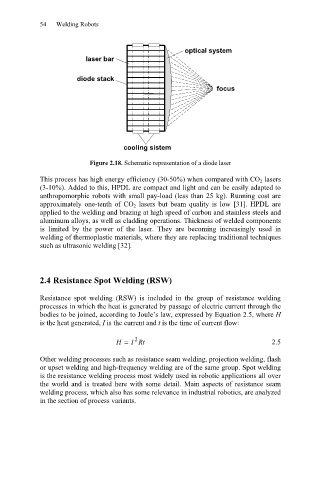
Figure 2.18. Schematic representation of a diode laser
This process has high energy efficiency (30-50%) when compared with CO 2 lasers
(3-10%). Added to this, HPDL are compact and light and can be easily adapted to
anthropomorphic robots with small pay-load (less than 25 kg). Running cost are
approximately one-tenth of CO 2 lasers but beam quality is low [31]. HPDL are
applied to the welding and brazing at high speed of carbon and stainless steels and
aluminum alloys, as well as cladding operations. Thickness of welded components
is limited by the power of the laser. They are becoming increasingly used in
welding of thermoplastic materials, where they are replacing traditional techniques
such as ultrasonic welding [32].
2.4 Resistance Spot Welding (RSW)
Resistance spot welding (RSW) is included in the group of resistance welding
processes in which the heat is generated by passage of electric current through the
bodies to be joined, according to Joule’s law, expressed by Equation 2.5, where H
is the heat generated, I is the current and t is the time of current flow:
H I 2 Rt 2.5
Other welding processes such as resistance seam welding, projection welding, flash
or upset welding and high-frequency welding are of the same group. Spot welding
is the resistance welding process most widely used in robotic applications all over
the world and is treated here with some detail. Main aspects of resistance seam
welding process, which also has some relevance in industrial robotics, are analyzed
in the section of process variants.