Page 76 - Welding Robots Technology, System Issues, and Applications
P. 76
61
Welding Technology
2.4.4 Process Variants
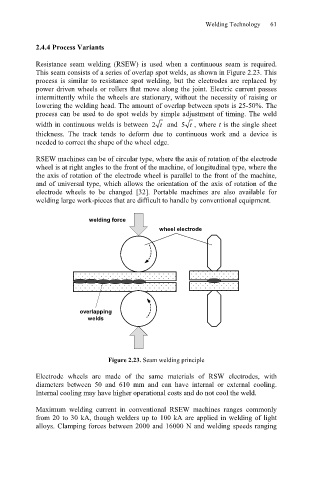
Resistance seam welding (RSEW) is used when a continuous seam is required.
This seam consists of a series of overlap spot welds, as shown in Figure 2.23. This
process is similar to resistance spot welding, but the electrodes are replaced by
power driven wheels or rollers that move along the joint. Electric current passes
intermittently while the wheels are stationary, without the necessity of raising or
lowering the welding head. The amount of overlap between spots is 25-50%. The
process can be used to do spot welds by simple adjustment of timing. The weld
width in continuous welds is between 2 t and 5 t , where t is the single sheet
thickness. The track tends to deform due to continuous work and a device is
needed to correct the shape of the wheel edge.
RSEW machines can be of circular type, where the axis of rotation of the electrode
wheel is at right angles to the front of the machine, of longitudinal type, where the
the axis of rotation of the electrode wheel is parallel to the front of the machine,
and of universal type, which allows the orientation of the axis of rotation of the
electrode wheels to be changed [32]. Portable machines are also available for
welding large work-pieces that are difficult to handle by conventional equipment.
welding force
wheel electrode
overlapping
welds
Figure 2.23. Seam welding principle
Electrode wheels are made of the same materials of RSW electrodes, with
diameters between 50 and 610 mm and can have internal or external cooling.
Internal cooling may have higher operational costs and do not cool the weld.
Maximum welding current in conventional RSEW machines ranges commonly
from 20 to 30 kA, though welders up to 100 kA are applied in welding of light
alloys. Clamping forces between 2000 and 16000 N and welding speeds ranging