Page 78 - Welding Robots Technology, System Issues, and Applications
P. 78
63
Welding Technology
2.5.1 Introduction
This welding process leads to the appearance of a thermo-mechanically affected
zone (TMAZ), which results from both plastic deformation and thermal exposure
of the material, and of a heat affected zone (HAZ), which only suffers the effect of
the thermal cycle. In the central part of the TMAZ there usually appears a distinct
nugget, having an onion ring feature, attributed to dynamic re-crystallization or
dynamic recovery of the microstructure [44].
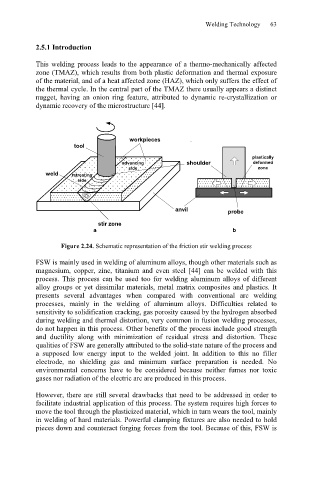
workpieces
tool
plastically
advancing shoulder deformed
side zone
weld retreating
side
anvil probe
stir zone
a b
Figure 2.24. Schematic representation of the friction stir welding process
FSW is mainly used in welding of aluminum alloys, though other materials such as
magnesium, copper, zinc, titanium and even steel [44] can be welded with this
process. This process can be used too for welding aluminum alloys of different
alloy groups or yet dissimilar materials, metal matrix composites and plastics. It
presents several advantages when compared with conventional arc welding
processes, mainly in the welding of aluminum alloys. Difficulties related to
sensitivity to solidification cracking, gas porosity caused by the hydrogen absorbed
during welding and thermal distortion, very common in fusion welding processes,
do not happen in this process. Other benefits of the process include good strength
and ductility along with minimization of residual stress and distortion. These
qualities of FSW are generally attributed to the solid-state nature of the process and
a supposed low energy input to the welded joint. In addition to this no filler
electrode, no shielding gas and minimum surface preparation is needed. No
environmental concerns have to be considered because neither fumes nor toxic
gases nor radiation of the electric arc are produced in this process.
However, there are still several drawbacks that need to be addressed in order to
facilitate industrial application of this process. The system requires high forces to
move the tool through the plasticized material, which in turn wears the tool, mainly
in welding of hard materials. Powerful clamping fixtures are also needed to hold
pieces down and counteract forging forces from the tool. Because of this, FSW is