Page 180 - Well Control for Completions and Interventions
P. 180
172 Well Control for Completions and Interventions
To BOP ram
closing chamber
From BOP ram
closing chamber From accumulator
From accumulator bottles (via) regulator
bottles (via) regulator
From BOP ram
opening chamber
To BOP ram
opening chamber
To Koomey unit
To Koomey unit reservoir
reservoir
Open Block Close
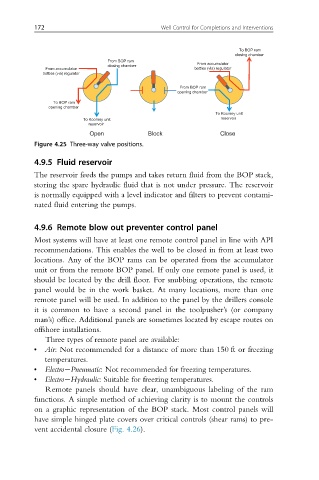
Figure 4.25 Three-way valve positions.
4.9.5 Fluid reservoir
The reservoir feeds the pumps and takes return fluid from the BOP stack,
storing the spare hydraulic fluid that is not under pressure. The reservoir
is normally equipped with a level indicator and filters to prevent contami-
nated fluid entering the pumps.
4.9.6 Remote blow out preventer control panel
Most systems will have at least one remote control panel in line with API
recommendations. This enables the well to be closed in from at least two
locations. Any of the BOP rams can be operated from the accumulator
unit or from the remote BOP panel. If only one remote panel is used, it
should be located by the drill floor. For snubbing operations, the remote
panel would be in the work basket. At many locations, more than one
remote panel will be used. In addition to the panel by the drillers console
it is common to have a second panel in the toolpusher’s (or company
man’s) office. Additional panels are sometimes located by escape routes on
offshore installations.
Three types of remote panel are available:
• Air: Not recommended for a distance of more than 150 ft or freezing
temperatures.
• Electro Pneumatic: Not recommended for freezing temperatures.
• Electro Hydraulic: Suitable for freezing temperatures.
Remote panels should have clear, unambiguous labeling of the ram
functions. A simple method of achieving clarity is to mount the controls
on a graphic representation of the BOP stack. Most control panels will
have simple hinged plate covers over critical controls (shear rams) to pre-
vent accidental closure (Fig. 4.26).