Page 170 - Well Logging and Formation Evaluation
P. 170
160 Well Logging and Formation Evaluation
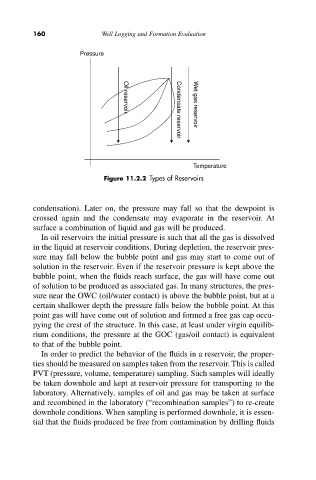
Pressure Oil reservoir Wet gas reservoir
Condensate reservoir
Temperature
Figure 11.2.2 Types of Reservoirs
condensation). Later on, the pressure may fall so that the dewpoint is
crossed again and the condensate may evaporate in the reservoir. At
surface a combination of liquid and gas will be produced.
In oil reservoirs the initial pressure is such that all the gas is dissolved
in the liquid at reservoir conditions. During depletion, the reservoir pres-
sure may fall below the bubble point and gas may start to come out of
solution in the reservoir. Even if the reservoir pressure is kept above the
bubble point, when the fluids reach surface, the gas will have come out
of solution to be produced as associated gas. In many structures, the pres-
sure near the OWC (oil/water contact) is above the bubble point, but at a
certain shallower depth the pressure falls below the bubble point. At this
point gas will have come out of solution and formed a free gas cap occu-
pying the crest of the structure. In this case, at least under virgin equilib-
rium conditions, the pressure at the GOC (gas/oil contact) is equivalent
to that of the bubble point.
In order to predict the behavior of the fluids in a reservoir, the proper-
ties should be measured on samples taken from the reservoir. This is called
PVT (pressure, volume, temperature) sampling. Such samples will ideally
be taken downhole and kept at reservoir pressure for transporting to the
laboratory. Alternatively, samples of oil and gas may be taken at surface
and recombined in the laboratory (“recombination samples”) to re-create
downhole conditions. When sampling is performed downhole, it is essen-
tial that the fluids produced be free from contamination by drilling fluids