Page 265 - Well Logging and Formation Evaluation
P. 265
Additional Mathematics Theory 255
120
100
80
GR 60
40
20
0
0 20 100 150 200 250 300
Depth (m)
500
450
400
350
300
A (I) 250
200
150
100
50
0
0 20 100 150 200 250 300
Wave number
2
1.5
1
0.5
phase –0.5 0 20 100 150 200 250 300
0
–1
–1.5
–2
Wave number
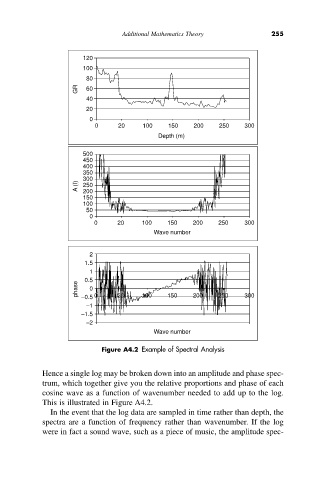
Figure A4.2 Example of Spectral Analysis
Hence a single log may be broken down into an amplitude and phase spec-
trum, which together give you the relative proportions and phase of each
cosine wave as a function of wavenumber needed to add up to the log.
This is illustrated in Figure A4.2.
In the event that the log data are sampled in time rather than depth, the
spectra are a function of frequency rather than wavenumber. If the log
were in fact a sound wave, such as a piece of music, the amplitude spec-