Page 222 - Whole Earth Geophysics An Introductory Textbook For Geologists And Geophysicists
P. 222
205
Interior
Earth’s
of
Probes
as
Seismic Waves
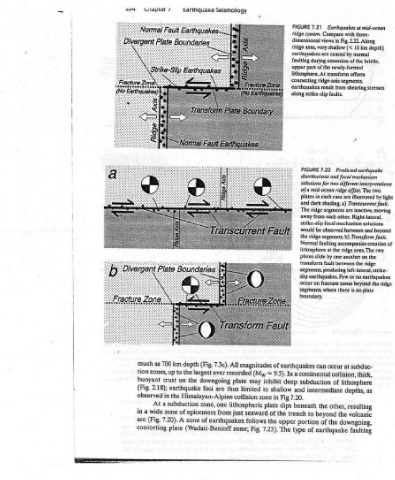
Earthquakes at mid-ocean Positions and types of 7.23 FIGURE three- Compare with earthquakes occurring at a subduction flexural bulge. Extension at a) zone, depth) 10 km up in zone Release of stress built b) Extension together. c) where plates lock intermediate to brittle, or compression in newly-formed portion of subducting plate. deep d) Compression as descending plate Compression encounters mesospher
7.21 dimensional views in Fig. 2.22. Along ridge axes, very shallow (< earthquakes are caused by normal faulting during extension of the upper part of the lithosphere. At transform offsets connecting ridge-axis segments, earthquakes result along strike-slip faults. 7.22 FIGURE of a mid-ocean in each case are and dark shading. a) strike-slip focal be observed ridge segments. b) Normal lithosphere at pla
FIGURE ridge system. plates The would the of earthquakes 9.5). In deep and shallow 7.20. Fig beneath dips trench the upper portion The type
magnitudes (My, ~ may inhibit limited to in zone lithospheric plate seaward of the follows 7.23). Fig,
Seismology (Fig. 7.3c). All ever recorded downgoing plate thus are Himalayan-Alpine collision one from just earthquakes zone;
-artnquake depth largest the foci zone, of epicenters zone of (Wadati-Benioff
km the to on earthquake the subduction A plate
/ 700 crust in a zone 7.20).
Knapter as much tion zones, up buoyant 2.18); (Fig. observed At ina wide arc (Fig. contorting
“ever