Page 225 - Whole Earth Geophysics An Introductory Textbook For Geologists And Geophysicists
P. 225
Refraction WN) High Apparent Velocity that ae ts in 2 = graphs in
207 “eiope” sie Earth’s on dis-
ae 2). be travel-time constant graphs for travel-time angular
Interior b) Series of a eit : ‘ ; functi the shallower rays. The changing wavefront the for The 1) reasons: with increase the
Earth's —s ea as a y than travel-time 7.25c. two because
of is modeled the travel-time graph. (Note:The earthquake seismology). abruptly the Fig. for generally
Probes events on travel-time graph. ee with depth than } in linear
as Jes more with depth, shown convex-upward, is
Waves arrivals curve V, forms seismic velocities graph surface.
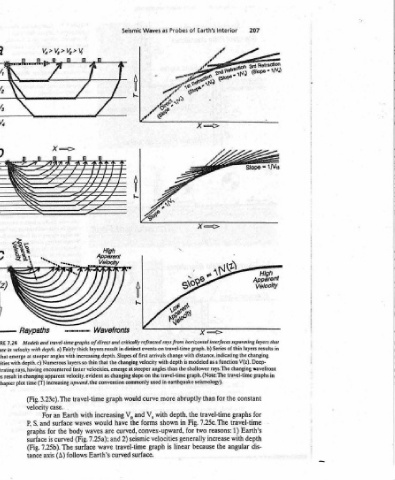
Seismic So Wavefronts Models and travel-time graphs of direct and critically refracted rays from horizontal interfaces separating Fairly thick layers result in distinct increasing depth. Slopes of first the changing velocity with that ts ened ieee velocities, emerge at steeper angles iti as changing slope on convention commonly used in would graph and in
ee === hin faster velocity, evident increasing upward. the travel-time with waves waves body 7.25a); (Fig. surface The Earth’s follows
V,>Vs>Vp>V — RaypathS a) velocity with depth. that emerge at steeper angles with h encountered having (T) time 3.23c). The (Fig. Ea ope an surface and S, the for graphs curved is surface 7.25b). (Fig. (A) axis tance
a v 7.24 FIGURE increase ‘ sn wi Jocities ys, i Pe ereuin Chain apparent chapter plot this P.
of from Earth, the as the of of the the of
regions the and and rigidity used be graph indicate thin layers, inter- traveled inverse function arrivals depth. function with travel-time from velocity repre- sur- curved effects accord- sta- raypaths measure- (inverse slope 180°) rays infinite the of Law
different distributions of regions (Vp Vs) and (k) can travel-time that very velocity higher ray the 3.34). The a thus path. The first with a as horizontally) the distance signifies the Fig. in 7.24 Earth’s the plotted recording to linear because velocity inverse the = (A graph; the center to Snell’s
traverse density of state velocities modulus bulk Chapter 4 in waves. A slopes with are many, deeper, the velocity 3.33, (Figs. is graph its of velocity described (travel line segments, with slope thus graphs waves, illustrate 7.25 are times epicenter 3 would follow curved, apparent 0°) ~ (A Earth the travel-time the to way according
S-waves and along with physical Chapter 3: k+ 4/3 p shear-wave Earth, the developed body segments When there angles for to relates layer travel-time deepest part increasing be can out discrete in at-‘@ny point travel-time earthquake Fig. in depth. Travel earthquake : waves be would how Notice epicenter side of the on all outward,
P- velocities, the in and the equations. theory of earthquake 7.24a). steeper emergence refracting the the indicating velocities bottom of decreasing curve point; and paths of models with the body. graph the Near opposite zero of downward, bend
Seismology which at seismic interpret to discussed Ver compressional within point the Earthquakes refraction travel the refraciing depth (Fig. emerge at of critically segments on encountered on curve. thin that 7.24a,b, waves 7.24c). Instead gradually of slope the deepest its The models travel The account. velocity from measured velocity, travel-time surface. curved distan
Earthquake the speeds These used be equations the known a for from for The Case analyze layers shows with rays angle Each of top the for any of the line wave convex-upward may so be Figs. (Fig. curve, of the encountered at Surface’ longer For into increasing constant had resulting Earth’s angular velocity. resulting thus gradually Taypaths the
suggests interior. can the if determined Layer to velocity refracted 7.24b). the at the As in depth z smooth inverse Earth Earth. taken as well distance surface. Earth The with true is velocity 7.25b).
7 data, to words, are (p) be Curves point horizontal in a on layers V(z). at a The wave be as angular the along changes the vertically, velocity
Chapter distances Earth’s gravity according and: other density (p.) can Flat Starting increase critically (Fig. faces horizontally slope of the velocity converge The depth, velocity is graph source. the Curved flat a must curvature to on the If 7.25a). are ments slope) represents emerge apparent the If (Fig.
206 In Travel-Time a for the that sent face ing tions (Fig. Earth