Page 226 - Whole Earth Geophysics An Introductory Textbook For Geologists And Geophysicists
P. 226
compressional wave penetrating the major
.
Selected raypath for
209
Interior
Earth’s
7.26
FIGURE
of
Probes
as
Seismic Waves
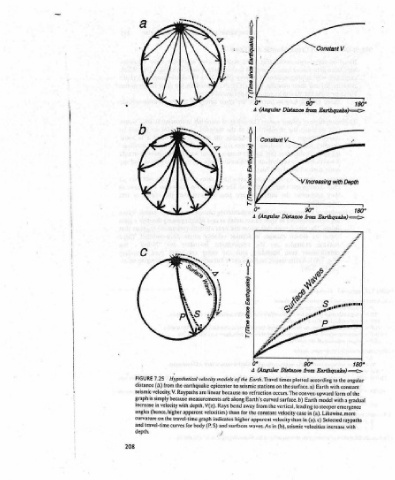
90° Distance from Earthquake) 90° Distance 90° Distance times plotted according to the surface. a) no refraction occurs. The convex-upward surface. b) Earth the vertical, leading to steeper Gaaccenes’ (a). in (a). c) in (b), seismic velocities
Constant V According to Snell’s Earth. zones of the sin®,/V,, where = Law, sind,/V; ray; velocity of incident = V, angle = velocity of refracted ray; 6; = V, of refraction. angle 0, = of incidence; layers, the three Within each of the seismic velocity increases with depth, so the vertical the ray bends away from that the (outward). Velocity drops abruptly at 80° 1 boundary, refracting
Constant Vv
1
eu)
<== (eyenbyez o° (Angular 4 S— (openixaeg cous out) 4 o° (Angular 4 <=> (ayenbyyez 1 ae (Angular A Earth. Travel Earth’s curved from bend away for the constant velocity case higher apparent velocity than
sous
eoujs
ew)
Hypothetical velocity models of the Raypaths are with depth, V(z). travel-time graph
eeoemomoms: ==, the earthquake epicenter to seismic stations on linear because measurements aré along Rays than velocities) indicates body (P,S) and surfaces waves. As in } it
: from because velocity (hence, higher apparent for
7.25 (A) velocity, V. is simply in curvature on the els curves
FIGURE distance seismic graph increase angles lepth.
208
ee