Page 75 - Whole Earth Geophysics An Introductory Textbook For Geologists And Geophysicists
P. 75
57 of com-
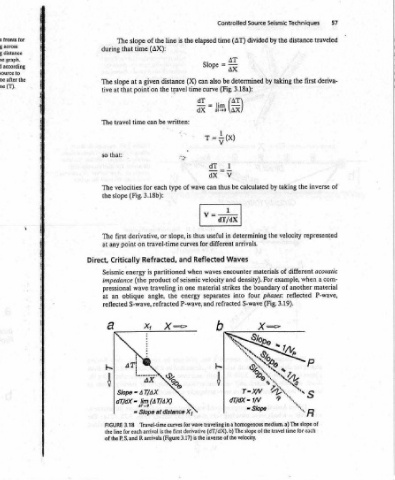
traveled deriva- inverse represented acoustic a material P-wave,
Techniques distance first the the different when another reflected for cach time
Seismic the by taking by taking by velocity the of example, For of phases: 3.19). (Fig. travel
Source divided determined calculated determining arrivals. materials density). boundary the four S-wave traveling in a homogenous medium. a) The slope of
Controlled (AT) time AT = aX be 3.18a): (Fig. (3) AX lim ato 1 T22 (x) _ V be thus 1 aT/ax in different Waves encounter and strikes into refracted (dT/dX). b) The slope of the inverse of the velocity.
elapsed Slope also can curve dT = — = dX av dX can wave = V useful thus for Reflected waves velocity material separates and the
the (X) time of is curves and when of seismic one energy P-wave, for wave derivative 3.17) is
is travel written: slope, in first
line distance type partitioned the refracted
the (AX): the be each or travel-time Refracted, product traveling angle, (AT/AX) = Slope at distance X; Travel-time curves is the arrivals (Figure
of given on can for 3.18b): is AT/AX lim arrival
slope time a at point time (Fig. derivative, on energy (the wave oblique S-wave, = dT/dX = 4T~0 for each
The that slope that at travel velocities slope first point Critically impedance pressional Slope 3.18 line P, S, and R
during The tive The that: so The the The any at Seismic an at reflected FIGURE the of the
Direct,
for to
fronts graph. according (T).
wave increasing distance plotted the source time side For the
Initial R waves, propagating across from each receiver. The elapsed time after the travel receiver refrac- Earth. from surface
a) at from the source. b) Travel-time (X) the is plotted each in
3.17 receivers The seismic traces are to the distance are to downward the time receiver the
FIGURE P,S,and several source is fired receivers source within travel curve: the to along
... the increasing depth the source
Traces of Receivers several from as to arrivals, travel-time the receiver, measured
Seismic for each the from (X) distance plotted relates often R-wave the by from travel the arrival. R
o Jt traces or to or
é 6 6 f=, \ Dispersion: Ranges commonly T to source PS,
x 5 (X) => 5 ——|____| seismic horizontal is because S-wave, linear, expressed the wave the the of
Waves 4 _ ff graph the (T) studies, P-wave, is for from velocity
Seismic R 'eCe, ive rs 3 tH Source 4 travel-time to time reflection initial receiver time total X= distance seismic
3 fi P From 3 a On according 3.17). Travel and the a to = T = V
Chapter Distance 2 - side, by (Fig. tion of each source where:
56 1
b (D) eu joAeLL —=