Page 76 - Whole Earth Geophysics An Introductory Textbook For Geologists And Geophysicists
P. 76
‘
a) Wave fronts are distorted from perfect
Raypaths thus bend (“‘refract”) across an
Refraction from layer of
material of different velocity (Fig. 3.15b).
spheres as energy is transmitted into
velocity (V,) to one of velocity (V,).
59
travel-time
V,
to
of
tak-
material
3.22a).
mate-
graph:
material:
material
'
velocity
by
Techniques
one
(Fig.
determined
travel-time
second
from
a
into
second
encounters
interface
on
Law:
3.22
travel
V,
the
arrival
Seismic
<
FIGURE
the
velocity
the
be
Snell’s
into
the
waves
can
on
in
energy
direct
transmitied
Source
across
(dT./dX)
fronts
material
to
material
of
seismic
according
4
V
the
of refracting medium.
Controlled
bend
seismic
wave
Vj
sin,
medium
dT,/dx
representing
i
Oy
near-surface
as
arrival
V,
be
raypaths
1
2
up
of raypaths
V,
_
refracted
from
may
When
speeds
sin@,
BT
dx
of incident
V,=
direct
Wi
energy
traveling
fronts,
line
Arrival
velocity
the
are
of the
bending
of refraction
of incidence
of
therefore:
the
straight
wave
3.22b), raypaths
velocity
velocity
velocity
wave
slope
of
Refracted
in
to
the
some
increase
the
perpendicular
a
of the
seismic
seismic
describes
is
For
the
angle
angle
velocity,
for
3.21b)
another.
that
Critically
inverse
3.19). An
equation
(Fig.
=
=
=
=
(Fig.
0,
Note
V,
V,
Refraction
6,
different
material
that:
remain
the
where:
to
graph
(Fig.
The
ing
rial
so
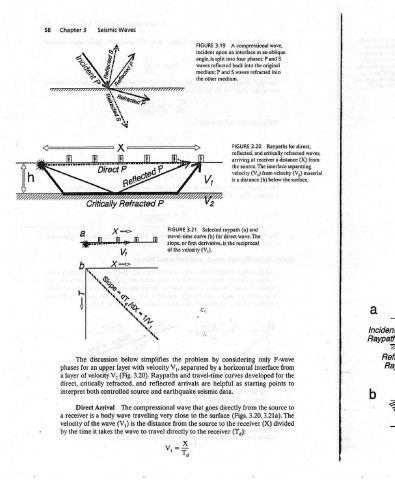
interface where velocity changes. b) The incident ‘2 refracted (6,) angles are (6,) and measured from a between the ndicular line drawn Refracted om to the interface Wave Fronts
Raypaths for direct, reflected, and critically refracted waves, from distance (X) interface separating material (V,) from velocity (V,) (h) below the surface. P-wave from the for to points to source 3.21a). The divided
compressional wave, interface at an oblique into four phases: P and S into the original refracted 3.20 receiver a source. The distance and wave. The reciprocal only interface developed starting the from 3.20, (X) receiver
into
A an back waves S FIGURE arriving at the velocity is a (a) raypath considering horizontal curves as data. directly (Figs. the (T,):
3.19 upon waves reflected the other medium. curve (b) for direct derivative, is the by a by helpful surface to receiver
FIGURE incident angle, is split medium: P and SS Selected 3.21 FIGURE travel-time slope, or first (V,). of the velocity problem the V,, separated travel-time and Raypaths are arrivals reflected seismic earthquake goes that wave the to close very source the from the to directly Xx Ma
Seismic Waves xX — e ete . Direct simplifies below discussion velocity with layer upper 3.20). (Fig. and refracted, and source controlled compressional The Arrival traveling wave body distance the is (V,) wave travel to wave the takes
3 el msmim isms The an for of velocity V, critically both Direct a is of the it time
Chapter Simtel phases ayer a direct, interpret receiver a velocity the by
58