Page 79 - Whole Earth Geophysics An Introductory Textbook For Geologists And Geophysicists
P. 79
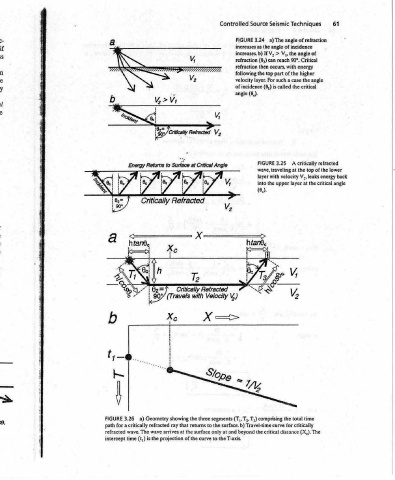
61 lower the critical angle
Techniques a) The angle of refraction V,, the angle of reach 90°. Critical energy higher the angle the critical Acritically refracted top of the the velocity V,, leaks energy back time for critically (X,). The
Seismic as the angle of incidence > If V, top part of the is called 3.25 wave, traveling at upper layer at distaace
Source 3.24 increases. b) refraction (8,) can refraction then occurs, with following the velocity layer. For such a case (6,) of incidence angle (6,). FIGURE layer with into the (0,). “Wy three segments (T,,T,,T;) comprising the total the critical
Controlled FIGURE in Angle Critically Refracted 4) Velocity => xX S/o LE ray that returns to the surface. b) Travel-time curve beyond the surface only at and the T-axis. to
Retums to Surface at Critical 82=)_ with (Travels 907 fin ae Geometry showing the a) 3.26 FIGURE path for a critically refracted wave. The wave arrives at refracted of the curve projection the is (t,) time intercept
veloc- if 2) across refraction angle occur only critical the lower surface are the be path: up
the interface; the the how the waves of can back increases across an
if increases of shows of the ahead (T,) travel and
1) the angle when can called = top to refracted wave the (T,); Refracted toward interface,
situations: from velocity the occurs refraction is 90° to the at returns arrive they refracted segments of layer 2 (c)
three away the if 3) does refraction, that critical refraction Snell’s Law materials: V, velocity Energy Critically distance, layer. three of top the same, and
describes refracted bent; interface. increases, so critical Note critical for in (8,) two sin(90°) Vv, with layer. 3.25). (Fig. at lower-velocity critically a the of the remains
Law tay is not is ray the incidence as necessary the of — traveling overlying angle because, upper, for time each along
Snell's the the toward of known (Fig. 3.24b). (0,) refraction of velocities sin®, Vv, sin8, vi sind, c wave, the in critical headwaves the travel in spent horizontally H Ray not bent. velocity (a) decreases, (b)
Waves how the interface, same, the bent is angle the situation, 90° Fig. 3.23c. of incidence angle the to refracted motions the at as only in that the the'time (T,); ray when
Seismic illustrates across remains the ray as special reaches (6,) in the relates particle inclined referred to travel shows adding 1 layer (T)). interface.
3.23 cases, A V,, as angle Setting critically that 3.26 by 1
3 Fig. decreases velocity interface, all In 3.24a). V, > The (6,). angle excites raypaths waves Fig. through layer Behavior of refracted
Chapter ity the the (Fig. of refraction when angle critical A layer, along sometimes direct calculated down through !
60 Retracted away from FIGURE 3.23 interface.