Page 206 - Wind Energy Handbook
P. 206
180 WIND-TURBINE PERFORMANCE
40
Electrical power (kW) 30
20
10 50rpm
45 rpm 55 rpm
60 rpm
0
0 5 6 7 8 9 10
Wind speed (m/s)
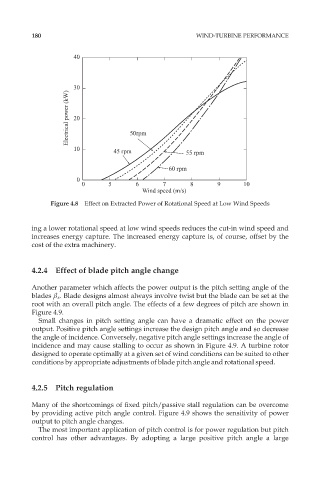
Figure 4.8 Effect on Extracted Power of Rotational Speed at Low Wind Speeds
ing a lower rotational speed at low wind speeds reduces the cut-in wind speed and
increases energy capture. The increased energy capture is, of course, offset by the
cost of the extra machinery.
4.2.4 Effect of blade pitch angle change
Another parameter which affects the power output is the pitch setting angle of the
blades â s . Blade designs almost always involve twist but the blade can be set at the
root with an overall pitch angle. The effects of a few degrees of pitch are shown in
Figure 4.9.
Small changes in pitch setting angle can have a dramatic effect on the power
output. Positive pitch angle settings increase the design pitch angle and so decrease
the angle of incidence. Conversely, negative pitch angle settings increase the angle of
incidence and may cause stalling to occur as shown in Figure 4.9. A turbine rotor
designed to operate optimally at a given set of wind conditions can be suited to other
conditions by appropriate adjustments of blade pitch angle and rotational speed.
4.2.5 Pitch regulation
Many of the shortcomings of fixed pitch/passive stall regulation can be overcome
by providing active pitch angle control. Figure 4.9 shows the sensitivity of power
output to pitch angle changes.
The most important application of pitch control is for power regulation but pitch
control has other advantages. By adopting a large positive pitch angle a large