Page 376 - Wind Energy Handbook
P. 376
350 CONCEPTUAL DESIGN OF HORIZONTAL-AXIS TURBINES
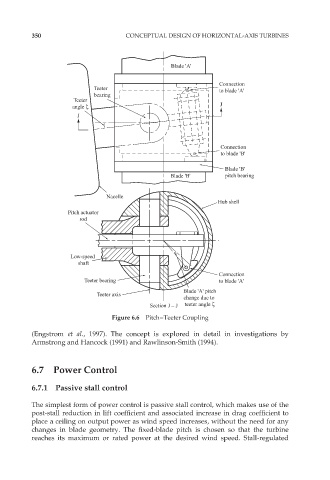
Blade 'A'
Connection
Teeter to blade 'A'
bearing
Teeter
angle J
J
Connection
to blade 'B'
Blade 'B'
Blade 'B' pitch bearing
Nacelle
Hub shell
Pitch actuator
rod
Low-speed
shaft
Connection
Teeter bearing to blade 'A'
Blade 'A' pitch
Teeter axis
change due to
SectionJ–J teeter angle ζ
Figure 6.6 Pitch–Teeter Coupling
(Engstrom et al., 1997). The concept is explored in detail in investigations by
Armstrong and Hancock (1991) and Rawlinson-Smith (1994).
6.7 Power Control
6.7.1 Passive stall control
The simplest form of power control is passive stall control, which makes use of the
post-stall reduction in lift coefficient and associated increase in drag coefficient to
place a ceiling on output power as wind speed increases, without the need for any
changes in blade geometry. The fixed-blade pitch is chosen so that the turbine
reaches its maximum or rated power at the desired wind speed. Stall-regulated