Page 148 - Characterization and Properties of Petroleum Fractions - M.R. Riazi
P. 148
P2: IML/FFX
T1: IML
QC: IML/FFX
P1: IML/FFX
June 22, 2007
AT029-Manual-v7.cls
AT029-03
AT029-Manual
14:23
128 CHARACTERIZATION AND PROPERTIES OF PETROLEUM FRACTIONS
molar additivity of structural contributions of carbon types
[58]. The correlation is derived from data on 61 oil fractions distillation data [4]:
with a squared correlation coefficient of 0.999 and average %H = (5.2407 + 0.01448T b − 7.018x A )/SG − 0.901x A
deviation of 3% and has the following form: (3.93) + 0.01298x A T b − 0.01345T b + 5.6879
82.952 − 65.341n 306 where x A is the fraction of aromatics in the mixture and
(3.92) %H = 30.346 + − T b is an average value of boiling points at 10, 50, and 90
d M
vol% vaporized in kelvin [T b = (T 10 + T 50 + T 90 )/3]. This cor-
where M is the molecular weight and n and d are refractive relation was developed based on 247 aviation fuels and 84
index and density at 20 C, respectively. This method should pure hydrocarbons. This method is quite accurate if all the
◦
be applied to fractions with molecular weight range of 84– input data are available from experimental measurement.
459, boiling point range of 60–480 C, refractive index range
◦
of 1.38–1.51, and hydrogen content of 12.2–15.6 wt%. In 3.5.2.1.4 Jenkins–Walsh Method—They developed a sim-
cases that M is not available it should be estimated from the ple relation in terms of specific gravity and aniline point in
Goossens correlation given by Eq. (2.55). the following form [59]:
(3.94) %H = 11.17 − 12.89SG + 0.0389AP
3.5.2.1.3 ASTM Method—ASTM describes a method to es-
timate the hydrogen content of aviation fuels under ASTM where AP is the aniline point in kelvin and it may be deter-
D 3343 test method based on the aromatic content and mined from the Winn nomograph (Fig. 2.14) presented in
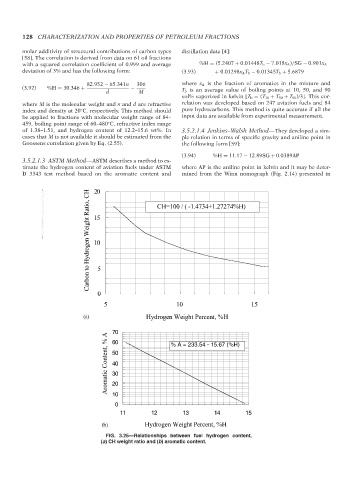
Carbon to Hydrogen Weight Ratio, CH 15
20
CH=100 / ( -1.4734+1.27274%H)
--`,```,`,``````,`,````,```,,-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---
10
5
0
5 10 15
(a) Hydrogen Weight Percent, %H
70 % A = 233.54 - 15.67 (%H)
Aromatic Content, % A 50
60
40
30
20
10
0
11 12 13 14 15
(b) Hydrogen Weight Percent, %H
FIG. 3.25—Relationships between fuel hydrogen content,
(a) CH weight ratio and (b) aromatic content.
Copyright ASTM International
Provided by IHS Markit under license with ASTM Licensee=International Dealers Demo/2222333001, User=Anggiansah, Erick
No reproduction or networking permitted without license from IHS Not for Resale, 08/26/2021 21:56:35 MDT