Page 74 - Algae Anatomy, Biochemistry, and Biotechnology
P. 74
Anatomy 57
FIGURE 2.27 Scanning electron microscopy image of the reservoir of E. gracilis in longitudinal section
showing the locomotory emerging flagellum bearing the photoreceptor and the nonemerging flagellum
reduced to a stub. (Bar: 0.50 mm.) (Courtesy of Dr. Franco Verni.)
the naked zoospore of Oedogonium, where the numerous flagella form a ring or crown around the
apical portion of the cell (stephanokont zoospore).
The characteristics of the flagella in a pair, that is, relative length and surface features, have led
to a specific nomenclature. When the two flagella differ in length and surface features, one being
hairy and the other smooth, they are termed “heterokont.” This term applies to all the members of
the division Heterokontophyta. When the two flagella are equal in length and appearance, the term
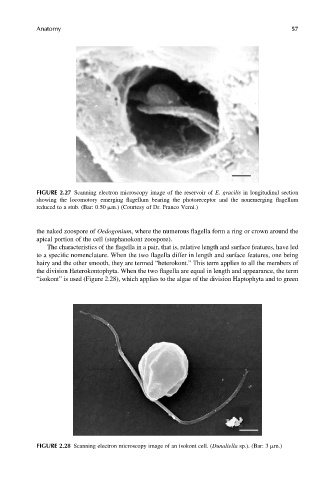
“isokont” is used (Figure 2.28), which applies to the algae of the division Haptophyta and to green
FIGURE 2.28 Scanning electron microscopy image of an isokont cell. (Dunaliella sp.). (Bar: 3 mm.)