Page 154 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 154
9 Life Cycle Inventory Analysis 139
A where the LCA supports a decision but the scale is small and market elasticities
make identification of the marginal product or technology uncertain in many cases.
9.3 Planning and Collection of Data
Based on the scope definition and the processes identified to belong within the
system boundaries, the collection of data for these processes has to be planned and
carried out. The planning has the purpose of balancing the effort of data collection
by the relevance of the respective data and information. This is essential in order to
avoid wasting time on collecting high-quality data that have a low relevance for the
LCA results and/or spend too little time on collecting high-quality data where it is
highly relevant for the results. Planning and collection of data are iterative pro-
cesses, which is why they are addressed together in this section. These processes are
an integrated part of the iterative approach to LCA that also involves the calculation
of LCIA results. For example, the first iteration of LCIA results may guide the
practitioner about which data are particularly relevant to focus on in a second
iteration.
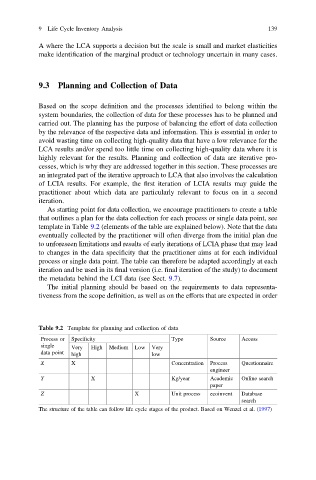
As starting point for data collection, we encourage practitioners to create a table
that outlines a plan for the data collection for each process or single data point, see
template in Table 9.2 (elements of the table are explained below). Note that the data
eventually collected by the practitioner will often diverge from the initial plan due
to unforeseen limitations and results of early iterations of LCIA phase that may lead
to changes in the data specificity that the practitioner aims at for each individual
process or single data point. The table can therefore be adapted accordingly at each
iteration and be used in its final version (i.e. final iteration of the study) to document
the metadata behind the LCI data (see Sect. 9.7).
The initial planning should be based on the requirements to data representa-
tiveness from the scope definition, as well as on the efforts that are expected in order
Table 9.2 Template for planning and collection of data
Process or Specificity Type Source Access
single Very High Medium Low Very
data point high low
X X Concentration Process Questionnaire
engineer
Y X Kg/year Academic Online search
paper
Z X Unit process ecoinvent Database
search
The structure of the table can follow life cycle stages of the product. Based on Wenzel et al. (1997)