Page 155 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 155
140 A. Bjørn et al.
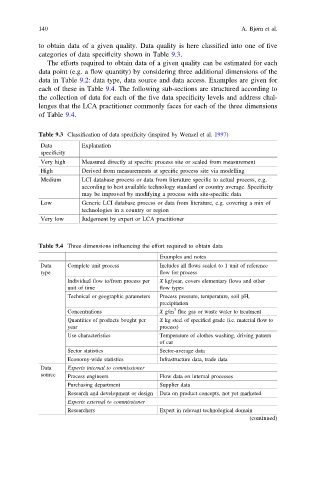
to obtain data of a given quality. Data quality is here classified into one of five
categories of data specificity shown in Table 9.3.
The efforts required to obtain data of a given quality can be estimated for each
data point (e.g. a flow quantity) by considering three additional dimensions of the
data in Table 9.2: data type, data source and data access. Examples are given for
each of these in Table 9.4. The following sub-sections are structured according to
the collection of data for each of the five data specificity levels and address chal-
lenges that the LCA practitioner commonly faces for each of the three dimensions
of Table 9.4.
Table 9.3 Classification of data specificity (inspired by Wenzel et al. 1997)
Data Explanation
specificity
Very high Measured directly at specific process site or scaled from measurement
High Derived from measurements at specific process site via modelling
Medium LCI database process or data from literature specific to actual process, e.g.
according to best available technology standard or country average. Specificity
may be improved by modifying a process with site-specific data
Low Generic LCI database process or data from literature, e.g. covering a mix of
technologies in a country or region
Very low Judgement by expert or LCA practitioner
Table 9.4 Three dimensions influencing the effort required to obtain data
Examples and notes
Data Complete unit process Includes all flows scaled to 1 unit of reference
type flow for process
Individual flow to/from process per X kg/year, covers elementary flows and other
unit of time flow types
Technical or geographic parameters Process pressure, temperature, soil pH,
precipitation
3
Concentrations X g/m flue gas or waste water to treatment
Quantities of products bought per X kg steel of specified grade (i.e. material flow to
year process)
Use characteristics Temperature of clothes washing, driving pattern
of car
Sector statistics Sector-average data
Economy-wide statistics Infrastructure data, trade data
Data Experts internal to commissioner
source Process engineers Flow data on internal processes
Purchasing department Supplier data
Research and development or design Data on product concepts, not yet marketed
Experts external to commissioner
Researchers Expert in relevant technological domain
(continued)