Page 467 -
P. 467
ACTIVATED CARBON PROCESSES 14.15
lOO
2o×3o
80 12 × 16
16 ~< 20 10x12
~ so
40
20
10 20 30 4o
BACKWASH RATE (gprn/f~
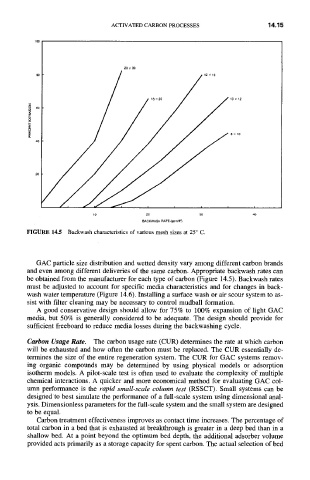
F|GURE 14.5 Backwash characteristics of various mesh sizes at 25 ° C.
GAC particle size distribution and wetted density vary among different carbon brands
and even among different deliveries of the same carbon. Appropriate backwash rates can
be obtained from the manufacturer for each type of carbon (Figure 14.5). Backwash rates
must be adjusted to account for specific media characteristics and for changes in back-
wash water temperature (Figure 14.6). Installing a surface wash or air scour system to as-
sist with filter cleaning may be necessary to control mudball formation.
A good conservative design should allow for 75% to 100% expansion of light GAC
media, but 50% is generally considered to be adequate. The design should provide for
sufficient freeboard to reduce media losses during the backwashing cycle.
Carbon Usage Rate. The carbon usage rate (CUR) determines the rate at which carbon
will be exhausted and how often the carbon must be replaced. The CUR essentially de-
termines the size of the entire regeneration system. The CUR for GAC systems remov-
ing organic compounds may be determined by using physical models or adsorption
isotherm models. A pilot-scale test is often used to evaluate the complexity of multiple
chemical interactions. A quicker and more economical method for evaluating GAC col-
umn performance is the rapid small-scale column test (RSSCT). Small systems can be
designed to best simulate the performance of a full-scale system using dimensional anal-
ysis. Dimensionless parameters for the full-scale system and the small system are designed
to be equal.
Carbon treatment effectiveness improves as contact time increases. The percentage of
total carbon in a bed that is exhausted at breakthrough is greater in a deep bed than in a
shallow bed. At a point beyond the optimum bed depth, the additional adsorber volume
provided acts primarily as a storage capacity for spent carbon. The actual selection of bed