Page 172 - A Comprehensive Guide to Solar Energy Systems
P. 172
Chapter 8 • Photovoltaics: The Basics 173
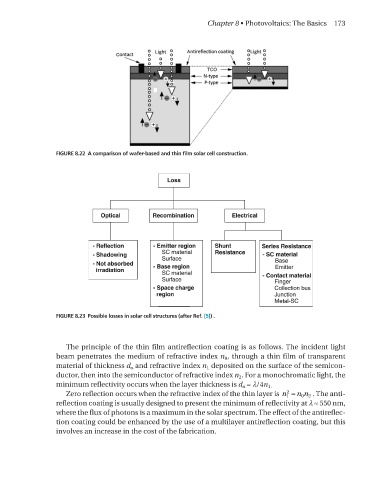
FIGURE 8.22 A comparison of wafer-based and thin film solar cell construction.
FIGURE 8.23 Possible losses in solar cell structures (after Ref. [5]) .
The principle of the thin film antireflection coating is as follows. The incident light
beam penetrates the medium of refractive index n 0 , through a thin film of transparent
material of thickness d a and refractive index n 1 deposited on the surface of the semicon-
ductor, then into the semiconductor of refractive index n 2 . For a monochromatic light, the
minimum reflectivity occurs when the layer thickness is d a = λ/4n 1.
Zero reflection occurs when the refractive index of the thin layer is n 1 2 = n n . The anti- n12=n 0 n 2
02
reflection coating is usually designed to present the minimum of reflectivity at λ ≈ 550 nm,
where the flux of photons is a maximum in the solar spectrum. The effect of the antireflec-
tion coating could be enhanced by the use of a multilayer antireflection coating, but this
involves an increase in the cost of the fabrication.