Page 406 -
P. 406
12 - PROJECT PROCUREMENT MANAGEMENT
Project Procurement Management
12.1
Plan
Procurement
Management
4.2
Develop Project • Procurement documents
Management • Project
Plan management
plan updates 12.2
Conduct Project
4.3 Procurements Documents
Direct and • Project
Manage Project management • Agreements
Work plan
• Project documents
• Work performance data updates
12.3
4.5
4.5 Control Perform
Perform • Approved change requests Procurements Integrated
Integrated • Change Change Control
Change Control requests
• Work
performance
reports • Organizational process
assets updates Enterprise/
4.4 Organization
Monitor and
Control Project
Work
• Work performance
information
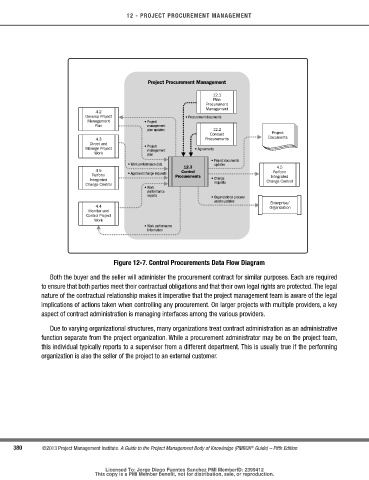
Figure 12-7. control Procurements data Flow diagram
Both the buyer and the seller will administer the procurement contract for similar purposes. Each are required
to ensure that both parties meet their contractual obligations and that their own legal rights are protected. The legal
nature of the contractual relationship makes it imperative that the project management team is aware of the legal
implications of actions taken when controlling any procurement. On larger projects with multiple providers, a key
aspect of contract administration is managing interfaces among the various providers.
Due to varying organizational structures, many organizations treat contract administration as an administrative
function separate from the project organization. While a procurement administrator may be on the project team,
this individual typically reports to a supervisor from a different department. This is usually true if the performing
organization is also the seller of the project to an external customer.
380 ©2013 Project Management Institute. A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide) – Fifth Edition
®
Licensed To: Jorge Diego Fuentes Sanchez PMI MemberID: 2399412
This copy is a PMI Member benefit, not for distribution, sale, or reproduction.