Page 62 - Hybrid Enhanced Oil Recovery Using Smart Waterflooding
P. 62
54 Hybrid Enhanced Oil Recovery using Smart Waterflooding
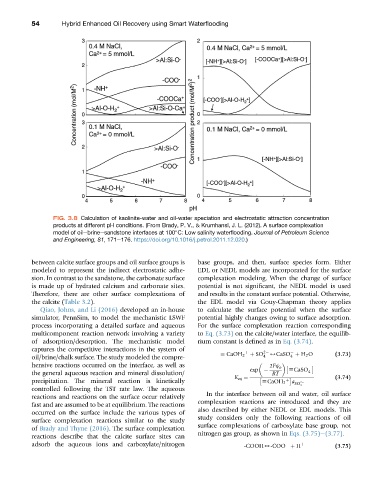
FIG. 3.8 Calculation of kaolinite-water and oil-water speciation and electrostatic attraction concentration
products at different pH conditions. (From Brady, P. V., & Krumhansl, J. L. (2012). A surface complexation
model of oilebrineesandstone interfaces at 100 C: Low salinity waterflooding. Journal of Petroleum Science
and Engineering, 81, 171e176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2011.12.020.)
between calcite surface groups and oil surface groups is base groups, and then, surface species form. Either
modeled to represent the indirect electrostatic adhe- EDL or NEDL models are incorporated for the surface
sion. In contrast to the sandstone, the carbonate surface complexation modeling. When the change of surface
is made up of hydrated calcium and carbonate sites. potential is not significant, the NEDL model is used
Therefore, there are other surface complexations of and results in the constant surface potential. Otherwise,
the calcite (Table 3.2). the EDL model via Gouy-Chapman theory applies
Qiao, Johns, and Li (2016) developed an in-house to calculate the surface potential when the surface
simulator, PennSim, to model the mechanistic LSWF potential highly changes owing to surface adsorption.
process incorporating a detailed surface and aqueous For the surface complexation reaction corresponding
multicomponent reaction network involving a variety to Eq. (3.73) on the calcite/water interface, the equilib-
of adsorption/desorption. The mechanistic model rium constant is defined as in Eq. (3.74).
captures the competitive interactions in the system of þ 2
4
oil/brine/chalk surface. The study modeled the compre- h CaOH 2 þ SO 4 4CaSO þ H 2 O (3.73)
hensive reactions occurred on the interface, as well as 2Fj o
exp hCaSO
4
the general aqueous reaction and mineral dissolution/ RT
K eq ¼ (3.74)
precipitation. The mineral reaction is kinetically hCaOH 2 þ a 2
SO 4
controlled following the TST rate law. The aqueous
In the interface between oil and water, oil surface
reactions and reactions on the surface occur relatively
complexation reactions are introduced and they are
fast and are assumed to be at equilibrium. The reactions
also described by either NEDL or EDL models. This
occurred on the surface include the various types of
study considers only the following reactions of oil
surface complexation reactions similar to the study
surface complexations of carboxylate base group, not
of Brady and Thyne (2016). The surface complexation
nitrogen gas group, as shown in Eqs. (3.75)e(3.77).
reactions describe that the calcite surface sites can
adsorb the aqueous ions and carboxylate/nitrogen -COOH4-COO þ H þ (3.75)