Page 64 - Hybrid Enhanced Oil Recovery Using Smart Waterflooding
P. 64
56 Hybrid Enhanced Oil Recovery using Smart Waterflooding
Fathi, Austad, & Strand, 2010; Strand et al., 2008;
Yousef et al., 2011) to validate the LSWF model in chalk
and limestone cores. Although the mechanistic simula-
tions using NEDL model accurately predict the three
experimental measurements (Austad et al., 2012; Fathi
et al., 2010; Strand et al., 2008), they fail to model
the oil-wet coreflooding of Yousef et al. (2011). Instead,
the mechanistic simulation using EDL model success-
fully reproduces the oil production from the coreflood-
ing experiment. The numerical modeling of wettability
modification accurately predicts the experimental
measurements. In addition, hypothetical simulations
using the history-matched coreflooding (Austad et al.,
2012; Strand et al., 2008; Yousef et al., 2011) investigate
the role of anhydrite dissolution on the wettability
modification. The concentration of adsorbed carboxylic
group on the calcite surface is monitored when diluted
seawater or diluted formation water is injected into the
limestone and chalk (Fig. 3.11). The limestone contains
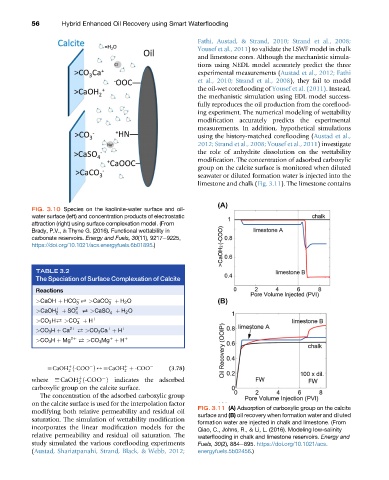
FIG. 3.10 Species on the kaolinite-water surface and oil-
water surface (left) and concentration products of electrostatic
attraction (right) using surface complexation model. (From
Brady, P.V., & Thyne G. (2016). Functional wettability in
carbonate reservoirs. Energy and Fuels, 30(11), 9217e9225,
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b01895.)
TABLE 3.2
The Speciation of Surface Complexation of Calcite
Reactions
>CaOH þ HCO % >CaCO þ H 2 O
3 3
>CaOH þ 2 þ SO 2 % >CaSO þ H 2 O
4
4
>CO 3 H% >CO 3 þ H þ
þ
>CO 3 H þ Ca 2þ % >CO 3 Ca þ H þ
>CO 3 H þ Mg 2þ % >CO 3 Mg þ H þ
þ
þ
hCaOH þ -COO 4hCaOH þ -COO (3.78)
2
2
þ
where hCaOH ð-COO Þ indicates the adsorbed
2
carboxylic group on the calcite surface.
The concentration of the adsorbed carboxylic group
on the calcite surface is used for the interpolation factor
modifying both relative permeability and residual oil FIG. 3.11 (A) Adsorption of carboxylic group on the calcite
surface and (B) oil recovery when formation water and diluted
saturation. The simulation of wettability modification formation water are injected in chalk and limestone. (From
incorporates the linear modification models for the Qiao, C., Johns, R., & Li, L. (2016). Modeling low-salinity
relative permeability and residual oil saturation. The waterflooding in chalk and limestone reservoirs. Energy and
study simulated the various coreflooding experiments Fuels, 30(2), 884e895. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.
(Austad, Shariatpanahi, Strand, Black, & Webb, 2012; energyfuels.5b02456.)