Page 94 - Hybrid Enhanced Oil Recovery Using Smart Waterflooding
P. 94
86 Hybrid Enhanced Oil Recovery using Smart Waterflooding
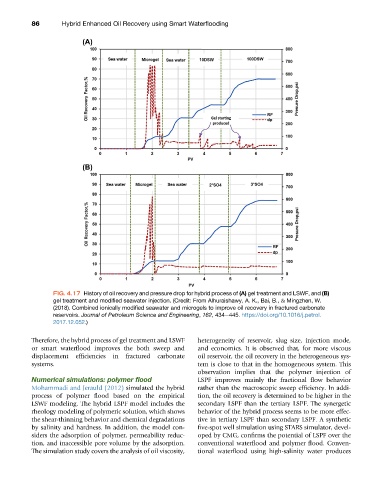
FIG. 4.17 History of oil recovery and pressure drop for hybrid process of (A) gel treatment and LSWF, and (B)
gel treatment and modified seawater injection. (Credit: From Alhuraishawy, A. K., Bai, B., & Mingzhen, W.
(2018). Combined ionically modified seawater and microgels to improve oil recovery in fractured carbonate
reservoirs. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 162, 434e445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.
2017.12.052.)
Therefore, the hybrid process of gel treatment and LSWF heterogeneity of reservoir, slug size, injection mode,
or smart waterflood improves the both sweep and and economics. It is observed that, for more viscous
displacement efficiencies in fractured carbonate oil reservoir, the oil recovery in the heterogeneous sys-
systems. tem is close to that in the homogeneous system. This
observation implies that the polymer injection of
Numerical simulations: polymer flood LSPF improves mainly the fractional flow behavior
Mohammadi and Jerauld (2012) simulated the hybrid rather than the macroscopic sweep efficiency. In addi-
process of polymer flood based on the empirical tion, the oil recovery is determined to be higher in the
LSWF modeling. The hybrid LSPF model includes the secondary LSPF than the tertiary LSPF. The synergetic
rheology modeling of polymeric solution, which shows behavior of the hybrid process seems to be more effec-
the shear-thinning behavior and chemical degradations tive in tertiary LSPF than secondary LSPF. A synthetic
by salinity and hardness. In addition, the model con- five-spot well simulation using STARS simulator, devel-
siders the adsorption of polymer, permeability reduc- oped by CMG, confirms the potential of LSPF over the
tion, and inaccessible pore volume by the adsorption. conventional waterflood and polymer flood. Conven-
The simulation study covers the analysis of oil viscosity, tional waterflood using high-salinity water produces