Page 74 - ARM 64 Bit Assembly Language
P. 74
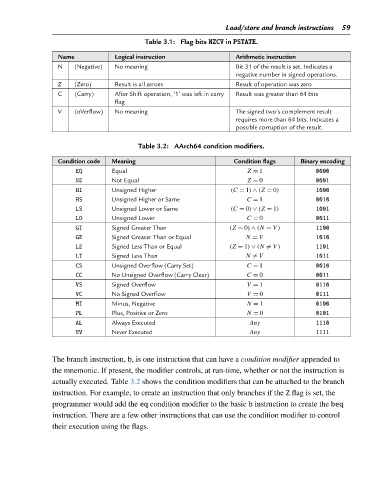
Load/store and branch instructions 59
Table 3.1: Flag bits NZCV in PSTATE.
Name Logical instruction Arithmetic instruction
N (Negative) No meaning Bit 31 of the result is set. Indicates a
negative number in signed operations.
Z (Zero) Result is all zeroes Result of operation was zero
C (Carry) After Shift operation, ‘1’ was left in carry Result was greater than 64 bits
flag
V (oVerflow) No meaning The signed two’s complement result
requires more than 64 bits. Indicates a
possible corruption of the result.
Table 3.2: AArch64 condition modifiers.
Condition code Meaning Condition flags Binary encoding
EQ Equal Z = 1 0000
NE Not Equal Z = 0 0001
HI Unsigned Higher (C = 1) ∧ (Z = 0) 1000
HS Unsigned Higher or Same C = 1 0010
LS Unsigned Lower or Same (C = 0) ∨ (Z = 1) 1001
LO Unsigned Lower C = 0 0011
GT Signed Greater Than (Z = 0) ∧ (N = V) 1100
GE Signed Greater Than or Equal N = V 1010
LE Signed Less Than or Equal (Z = 1) ∨ (N = V) 1101
LT Signed Less Than N = V 1011
CS Unsigned Overflow (Carry Set) C = 1 0010
CC No Unsigned Overflow (Carry Clear) C = 0 0011
VS Signed Overflow V = 1 0110
VC No Signed Overflow V = 0 0111
MI Minus, Negative N = 1 0100
PL Plus, Positive or Zero N = 0 0101
AL Always Executed Any 1110
NV Never Executed Any 1111
The branch instruction, b, is one instruction that can have a condition modifier appended to
the mnemonic. If present, the modifier controls, at run-time, whether or not the instruction is
actually executed. Table 3.2 shows the condition modifiers that can be attached to the branch
instruction. For example, to create an instruction that only branches if the Z flag is set, the
programmer would add the eq condition modifier to the basic b instruction to create the beq
instruction. There are a few other instructions that can use the condition modifier to control
their execution using the flags.