Page 76 - ARM 64 Bit Assembly Language
P. 76
Load/store and branch instructions 61
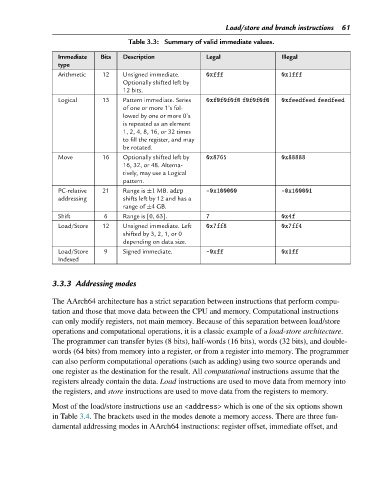
Table 3.3: Summary of valid immediate values.
Immediate Bits Description Legal Illegal
type
Arithmetic 12 Unsigned immediate. 0xfff 0x1fff
Optionally shifted left by
12 bits.
Logical 13 Pattern immediate. Series 0xf0f0f0f0 f0f0f0f0 0xfeedfeed feedfeed
of one or more 1’s fol-
lowed by one or more 0’s
is repeated as an element
1, 2, 4, 8, 16, or 32 times
to fill the register, and may
be rotated.
Move 16 Optionally shifted left by 0x8765 0x88888
16, 32, or 48. Alterna-
tively, may use a Logical
pattern.
PC-relative 21 Range is ±1 MB. adrp -0x100000 -0x100001
addressing shifts left by 12 and has a
range of ±4 GB.
Shift 6 Range is [0, 63]. 7 0x4f
Load/Store 12 Unsigned immediate. Left 0x7ff8 0x7ff4
shiftedby3,2,1,or0
depending on data size.
Load/Store 9 Signed immediate. -0xff 0x1ff
Indexed
3.3.3 Addressing modes
The AArch64 architecture has a strict separation between instructions that perform compu-
tation and those that move data between the CPU and memory. Computational instructions
can only modify registers, not main memory. Because of this separation between load/store
operations and computational operations, it is a classic example of a load-store architecture.
The programmer can transfer bytes (8 bits), half-words (16 bits), words (32 bits), and double-
words (64 bits) from memory into a register, or from a register into memory. The programmer
can also perform computational operations (such as adding) using two source operands and
one register as the destination for the result. All computational instructions assume that the
registers already contain the data. Load instructions are used to move data from memory into
the registers, and store instructions are used to move data from the registers to memory.
Most of the load/store instructions use an <address> which is one of the six options shown
in Table 3.4. The brackets used in the modes denote a memory access. There are three fun-
damental addressing modes in AArch64 instructions: register offset, immediate offset, and