Page 356 - Accounting Information Systems
P. 356
C H A P TER 7 The Conversion Cycle 327
FI G U R E
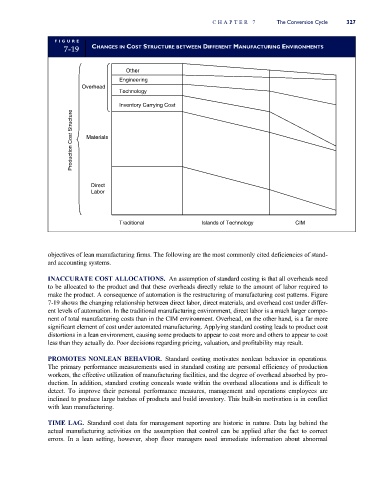
7-19 CHANGES IN COST STRUCTURE BETWEEN DIFFERENT MANUFACTURING ENVIRONMENTS
Other
Engineering
Overhead
Technology
Inventory Carrying Cost
Production Cost Structure Materials
Direct
Labor
Traditional Islands of Technology CIM
objectives of lean manufacturing firms. The following are the most commonly cited deficiencies of stand-
ard accounting systems.
INACCURATE COST ALLOCATIONS. An assumption of standard costing is that all overheads need
to be allocated to the product and that these overheads directly relate to the amount of labor required to
make the product. A consequence of automation is the restructuring of manufacturing cost patterns. Figure
7-19 shows the changing relationship between direct labor, direct materials, and overhead cost under differ-
ent levels of automation. In the traditional manufacturing environment, direct labor is a much larger compo-
nent of total manufacturing costs than in the CIM environment. Overhead, on the other hand, is a far more
significant element of cost under automated manufacturing. Applying standard costing leads to product cost
distortions in a lean environment, causing some products to appear to cost more and others to appear to cost
less than they actually do. Poor decisions regarding pricing, valuation, and profitability may result.
PROMOTES NONLEAN BEHAVIOR. Standard costing motivates nonlean behavior in operations.
The primary performance measurements used in standard costing are personal efficiency of production
workers, the effective utilization of manufacturing facilities, and the degree of overhead absorbed by pro-
duction. In addition, standard costing conceals waste within the overhead allocations and is difficult to
detect. To improve their personal performance measures, management and operations employees are
inclined to produce large batches of products and build inventory. This built-in motivation is in conflict
with lean manufacturing.
TIME LAG. Standard cost data for management reporting are historic in nature. Data lag behind the
actual manufacturing activities on the assumption that control can be applied after the fact to correct
errors. In a lean setting, however, shop floor managers need immediate information about abnormal