Page 197 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 197
188 3. NOISE IN MARINE SEISMICS
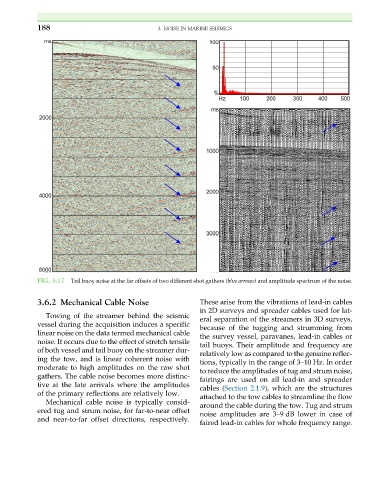
FIG. 3.17 Tail buoy noise at the far offsets of two different shot gathers (blue arrows) and amplitude spectrum of the noise.
3.6.2 Mechanical Cable Noise These arise from the vibrations of lead-in cables
in 2D surveys and spreader cables used for lat-
Towing of the streamer behind the seismic eral separation of the streamers in 3D surveys,
vessel during the acquisition induces a specific because of the tugging and strumming from
linear noise on the data termed mechanical cable
the survey vessel, paravanes, lead-in cables or
noise. It occurs due to the effect of stretch tensile
tail buoys. Their amplitude and frequency are
of both vessel and tail buoy on the streamer dur-
relatively low as compared to the genuine reflec-
ing the tow, and is linear coherent noise with
tions, typically in the range of 3–10 Hz. In order
moderate to high amplitudes on the raw shot
to reduce the amplitudes of tug and strum noise,
gathers. The cable noise becomes more distinc-
fairings are used on all lead-in and spreader
tive at the late arrivals where the amplitudes
cables (Section 2.1.9), which are the structures
of the primary reflections are relatively low.
attached to the tow cables to streamline the flow
Mechanical cable noise is typically consid-
around the cable during the tow. Tug and strum
ered tug and strum noise, for far-to-near offset
noise amplitudes are 3–9 dB lower in case of
and near-to-far offset directions, respectively.
faired lead-in cables for whole frequency range.