Page 202 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 202
3.8 GUIDED WAVES 193
information of the topmost sedimentary unit. gathers. Similar diffraction hyperbolas are also
Relatively long offsets are required to record obtained from suddenly terminated layers, such
refracted waves, since it is necessary for them as at fault planes or pinch-outs. Therefore, fault
to refract, to travel horizontally, and to refract planes on the nonmigrated stack sections are
again to arrive at the streamer (Section 1.3.3). characterized by a series of diffraction hyper-
Therefore, they can be observed at relatively bolas. These hyperbolas can be completely
shallower waters with longer streamers. They removed by a suitable migration algorithm,
always appear before the seabed reflection which sums up the diffraction energy to the apex
hyperbola like direct waves and can be removed point providing that a correct velocity field for
by a top mute (Section 5.8). whole seismic line is known (Chapter 11).
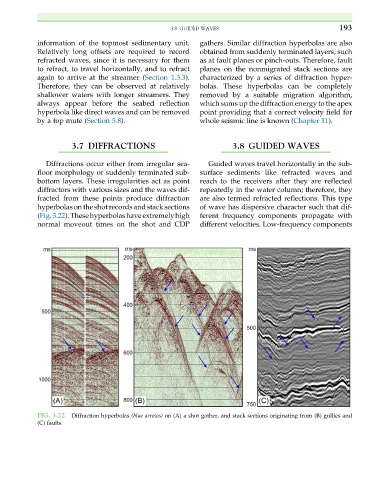
3.7 DIFFRACTIONS 3.8 GUIDED WAVES
Diffractions occur either from irregular sea- Guided waves travel horizontally in the sub-
floor morphology or suddenly terminated sub- surface sediments like refracted waves and
bottom layers. These irregularities act as point reach to the receivers after they are reflected
diffractors with various sizes and the waves dif- repeatedly in the water column; therefore, they
fracted from these points produce diffraction are also termed refracted reflections. This type
hyperbolas on the shot records and stack sections of wave has dispersive character such that dif-
(Fig.3.22).Thesehyperbolashaveextremelyhigh ferent frequency components propagate with
normal moveout times on the shot and CDP different velocities. Low-frequency components
FIG. 3.22 Diffraction hyperbolas (blue arrows) on (A) a shot gather, and stack sections originating from (B) gullies and
(C) faults.