Page 200 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 200
3.6 INLINE WAVES 191
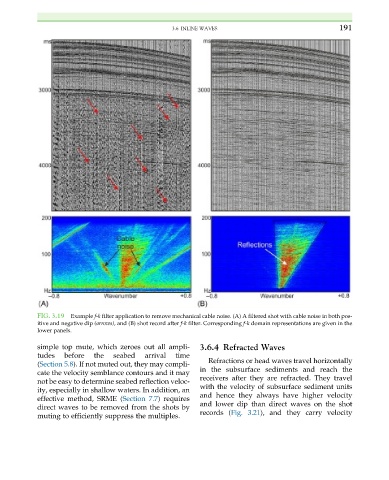
FIG. 3.19 Example f-k filter application to remove mechanical cable noise. (A) A filtered shot with cable noise in both pos-
itive and negative dip (arrows), and (B) shot record after f-k filter. Corresponding f-k domain representations are given in the
lower panels.
simple top mute, which zeroes out all ampli- 3.6.4 Refracted Waves
tudes before the seabed arrival time
(Section 5.8). If not muted out, they may compli- Refractions or head waves travel horizontally
cate the velocity semblance contours and it may in the subsurface sediments and reach the
receivers after they are refracted. They travel
not be easy to determine seabed reflection veloc-
with the velocity of subsurface sediment units
ity, especially in shallow waters. In addition, an
effective method, SRME (Section 7.7) requires and hence they always have higher velocity
direct waves to be removed from the shots by and lower dip than direct waves on the shot
muting to efficiently suppress the multiples. records (Fig. 3.21), and they carry velocity