Page 211 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 211
202 3. NOISE IN MARINE SEISMICS
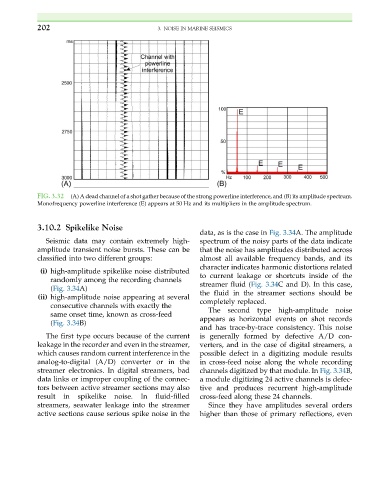
FIG. 3.32 (A) A dead channel of a shot gather because of the strong powerline interference, and (B) its amplitude spectrum.
Monofrequency powerline interference (E) appears at 50 Hz and its multipliers in the amplitude spectrum.
3.10.2 Spikelike Noise
data, as is the case in Fig. 3.34A. The amplitude
Seismic data may contain extremely high- spectrum of the noisy parts of the data indicate
amplitude transient noise bursts. These can be that the noise has amplitudes distributed across
classified into two different groups: almost all available frequency bands, and its
character indicates harmonic distortions related
(i) high-amplitude spikelike noise distributed
to current leakage or shortcuts inside of the
randomly among the recording channels
(Fig. 3.34A) streamer fluid (Fig. 3.34C and D). In this case,
(ii) high-amplitude noise appearing at several the fluid in the streamer sections should be
consecutive channels with exactly the completely replaced.
same onset time, known as cross-feed The second type high-amplitude noise
(Fig. 3.34B) appears as horizontal events on shot records
and has trace-by-trace consistency. This noise
The first type occurs because of the current is generally formed by defective A/D con-
leakage in the recorder and even in the streamer, verters, and in the case of digital streamers, a
which causes random current interference in the possible defect in a digitizing module results
analog-to-digital (A/D) converter or in the in cross-feed noise along the whole recording
streamer electronics. In digital streamers, bad channels digitized by that module. In Fig. 3.34B,
data links or improper coupling of the connec- a module digitizing 24 active channels is defec-
tors between active streamer sections may also tive and produces recurrent high-amplitude
result in spikelike noise. In fluid-filled cross-feed along these 24 channels.
streamers, seawater leakage into the streamer Since they have amplitudes several orders
active sections cause serious spike noise in the higher than those of primary reflections, even