Page 209 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 209
200 3. NOISE IN MARINE SEISMICS
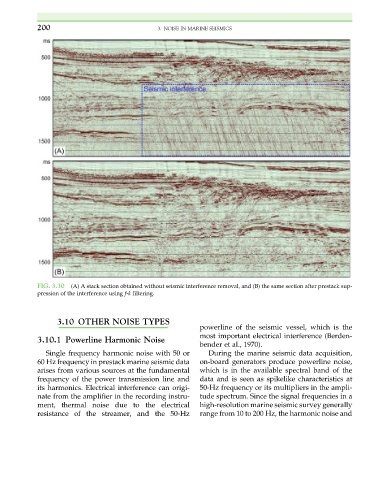
FIG. 3.30 (A) A stack section obtained without seismic interference removal, and (B) the same section after prestack sup-
pression of the interference using f-k filtering.
3.10 OTHER NOISE TYPES
powerline of the seismic vessel, which is the
most important electrical interference (Berden-
3.10.1 Powerline Harmonic Noise
bender et al., 1970).
Single frequency harmonic noise with 50 or During the marine seismic data acquisition,
60 Hz frequency in prestack marine seismic data on-board generators produce powerline noise,
arises from various sources at the fundamental which is in the available spectral band of the
frequency of the power transmission line and data and is seen as spikelike characteristics at
its harmonics. Electrical interference can origi- 50-Hz frequency or its multipliers in the ampli-
nate from the amplifier in the recording instru- tude spectrum. Since the signal frequencies in a
ment, thermal noise due to the electrical high-resolution marine seismic survey generally
resistance of the streamer, and the 50-Hz range from 10 to 200 Hz, the harmonic noise and