Page 282 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 282
5.6 GAIN RECOVERY 273
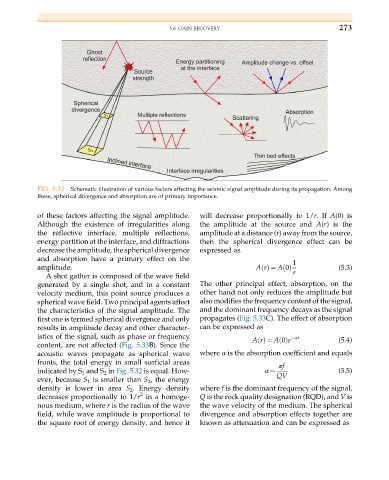
FIG. 5.32 Schematic illustration of various factors affecting the seismic signal amplitude during its propagation. Among
these, spherical divergence and absorption are of primary importance.
of these factors affecting the signal amplitude. will decrease proportionally to 1/r.If A(0) is
Although the existence of irregularities along the amplitude at the source and A(r) is the
the reflective interface, multiple reflections, amplitude at a distance (r) away from the source,
energy partition at the interface, and diffractions then the spherical divergence effect can be
decrease the amplitude, the spherical divergence expressed as
and absorption have a primary effect on the 1
amplitude. ArðÞ ¼ A 0ðÞ (5.3)
A shot gather is composed of the wave field r
generated by a single shot, and in a constant The other principal effect, absorption, on the
velocity medium, this point source produces a other hand not only reduces the amplitude but
spherical wave field. Two principal agents affect also modifies the frequency content of the signal,
the characteristics of the signal amplitude. The and the dominant frequency decays as the signal
first one is termed spherical divergence and only propagates (Fig. 5.33C). The effect of absorption
results in amplitude decay and other character- can be expressed as
istics of the signal, such as phase or frequency αr
ArðÞ ¼ A 0ðÞe (5.4)
content, are not affected (Fig. 5.33B). Since the
acoustic waves propagate as spherical wave where α is the absorption coefficient and equals
fronts, the total energy in small surficial areas
πf
indicated by S 1 and S 2 in Fig. 5.32 is equal. How- α ¼ (5.5)
QV
ever, because S 1 is smaller than S 2 , the energy
density is lower in area S 2 . Energy density where f is the dominant frequency of the signal,
2
decreases proportionally to 1/r in a homoge- Q is the rock quality designation (RQD), and V is
nous medium, where r is the radius of the wave the wave velocity of the medium. The spherical
field, while wave amplitude is proportional to divergence and absorption effects together are
the square root of energy density, and hence it known as attenuation and can be expressed as