Page 317 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 317
308 5. PREPROCESSING
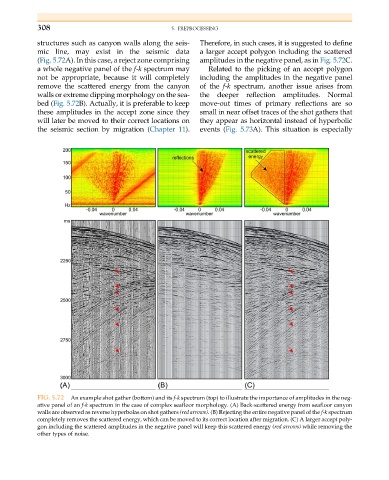
structures such as canyon walls along the seis- Therefore, in such cases, it is suggested to define
mic line, may exist in the seismic data a larger accept polygon including the scattered
(Fig. 5.72A). In this case, a reject zone comprising amplitudes in the negative panel, as in Fig. 5.72C.
a whole negative panel of the f-k spectrum may Related to the picking of an accept polygon
not be appropriate, because it will completely including the amplitudes in the negative panel
remove the scattered energy from the canyon of the f-k spectrum, another issue arises from
walls or extreme dipping morphology on the sea- the deeper reflection amplitudes. Normal
bed (Fig. 5.72B). Actually, it is preferable to keep move-out times of primary reflections are so
these amplitudes in the accept zone since they small in near offset traces of the shot gathers that
will later be moved to their correct locations on they appear as horizontal instead of hyperbolic
the seismic section by migration (Chapter 11). events (Fig. 5.73A). This situation is especially
FIG. 5.72 An example shot gather (bottom) and its f-k spectrum (top) to illustrate the importance of amplitudes in the neg-
ative panel of an f-k spectrum in the case of complex seafloor morphology. (A) Back-scattered energy from seafloor canyon
walls are observed as reverse hyperbolas on shot gathers (red arrows). (B) Rejecting the entire negative panel of the f-k spectrum
completely removes the scattered energy, which can be moved to its correct location after migration. (C) A larger accept poly-
gon including the scattered amplitudes in the negative panel will keep this scattered energy (red arrows) while removing the
other types of noise.