Page 387 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 387
378 7. SUPPRESSION OF MULTIPLE REFLECTIONS
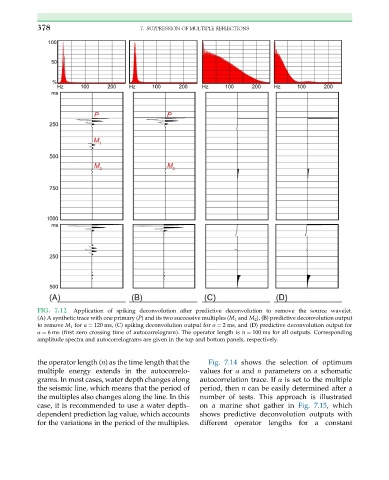
FIG. 7.12 Application of spiking deconvolution after predictive deconvolution to remove the source wavelet.
(A) A synthetic trace with one primary (P) and its two successive multiples (M 1 and M 2 ), (B) predictive deconvolution output
to remove M 1 for α ¼ 120 ms, (C) spiking deconvolution output for α ¼ 2 ms, and (D) predictive deconvolution output for
α ¼ 6 ms (first zero crossing time of autocorrelogram). The operator length is n ¼ 100 ms for all outputs. Corresponding
amplitude spectra and autocorrelograms are given in the top and bottom panels, respectively.
the operator length (n) as the time length that the Fig. 7.14 shows the selection of optimum
multiple energy extends in the autocorrelo- values for α and n parameters on a schematic
grams. In most cases, water depth changes along autocorrelation trace. If α is set to the multiple
the seismic line, which means that the period of period, then n can be easily determined after a
the multiples also changes along the line. In this number of tests. This approach is illustrated
case, it is recommended to use a water depth– on a marine shot gather in Fig. 7.15, which
dependent prediction lag value, which accounts shows predictive deconvolution outputs with
for the variations in the period of the multiples. different operator lengths for a constant