Page 476 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 476
10.1 NORMAL MOVEOUT TIME 467
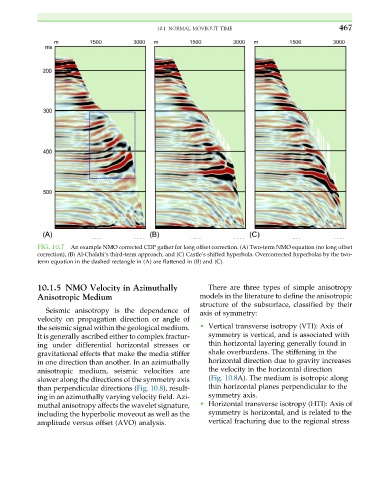
FIG. 10.7 An example NMO corrected CDP gather for long offset correction. (A) Two-term NMO equation (no long offset
correction), (B) Al-Chalabi’s third-term approach, and (C) Castle’s shifted hyperbola. Overcorrected hyperbolas by the two-
term equation in the dashed rectangle in (A) are flattened in (B) and (C).
10.1.5 NMO Velocity in Azimuthally There are three types of simple anisotropy
Anisotropic Medium models in the literature to define the anisotropic
structure of the subsurface, classified by their
Seismic anisotropy is the dependence of
axis of symmetry:
velocity on propagation direction or angle of
the seismic signal within the geological medium. • Vertical transverse isotropy (VTI): Axis of
It is generally ascribed either to complex fractur- symmetry is vertical, and is associated with
ing under differential horizontal stresses or thin horizontal layering generally found in
gravitational effects that make the media stiffer shale overburdens. The stiffening in the
in one direction than another. In an azimuthally horizontal direction due to gravity increases
anisotropic medium, seismic velocities are the velocity in the horizontal direction
slower along the directions of the symmetry axis (Fig. 10.8A). The medium is isotropic along
than perpendicular directions (Fig. 10.8), result- thin horizontal planes perpendicular to the
ing in an azimuthally varying velocity field. Azi- symmetry axis.
muthal anisotropy affects the wavelet signature, • Horizontal transverse isotropy (HTI): Axis of
including the hyperbolic moveout as well as the symmetry is horizontal, and is related to the
amplitude versus offset (AVO) analysis. vertical fracturing due to the regional stress